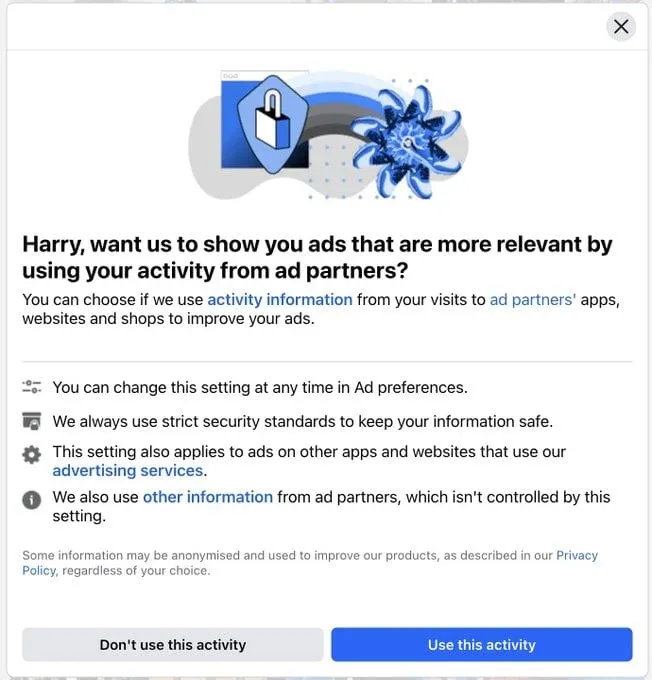
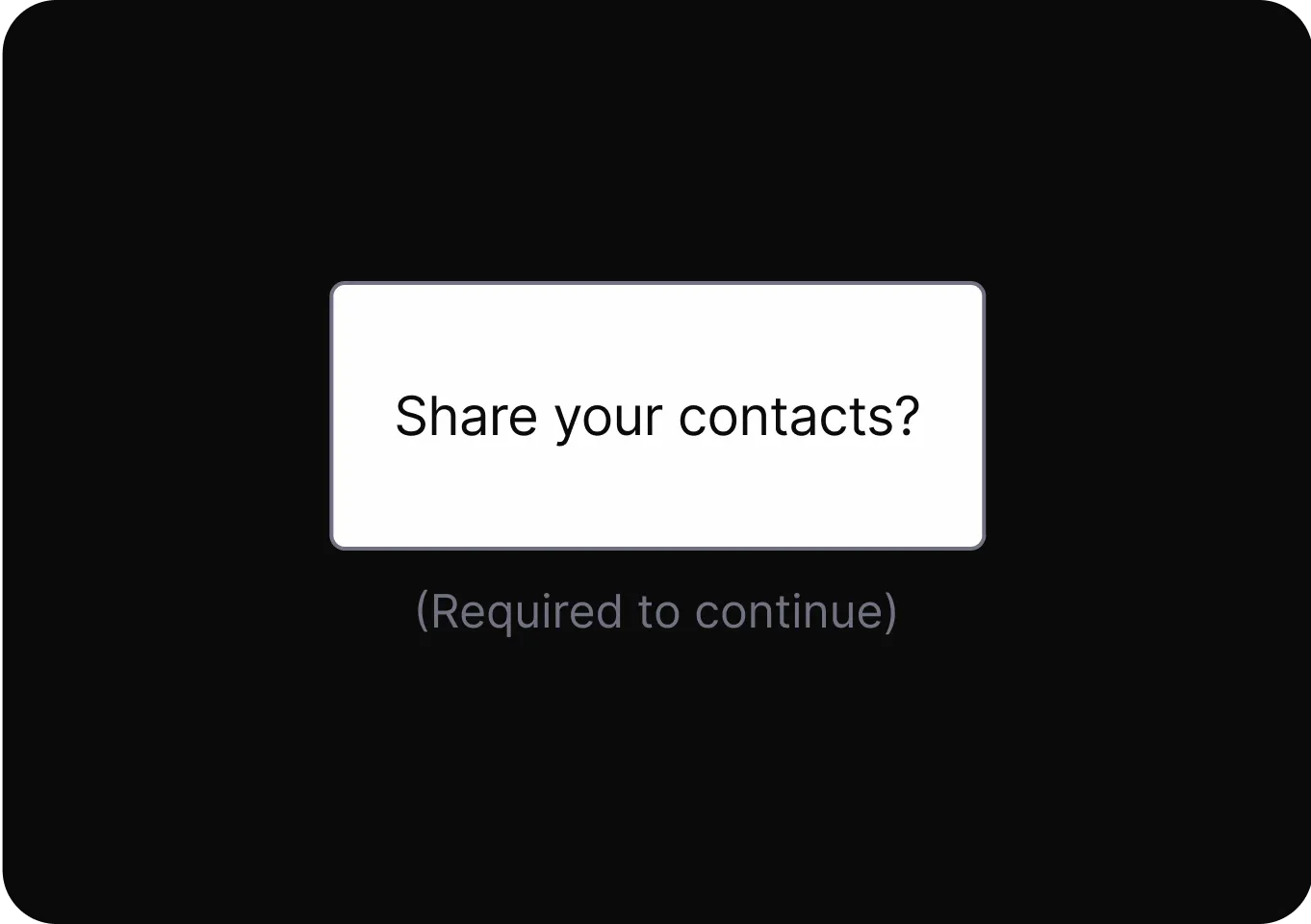
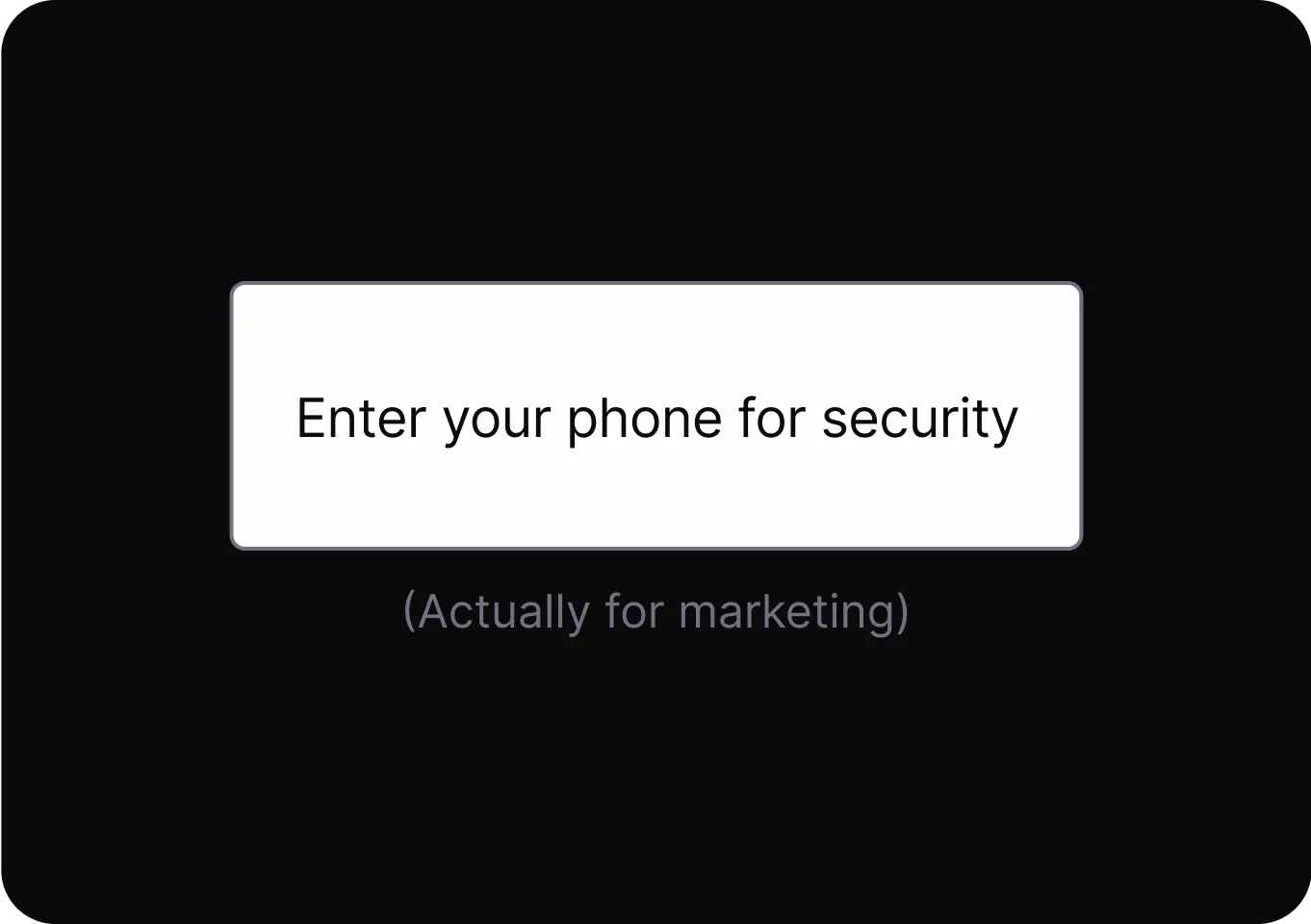
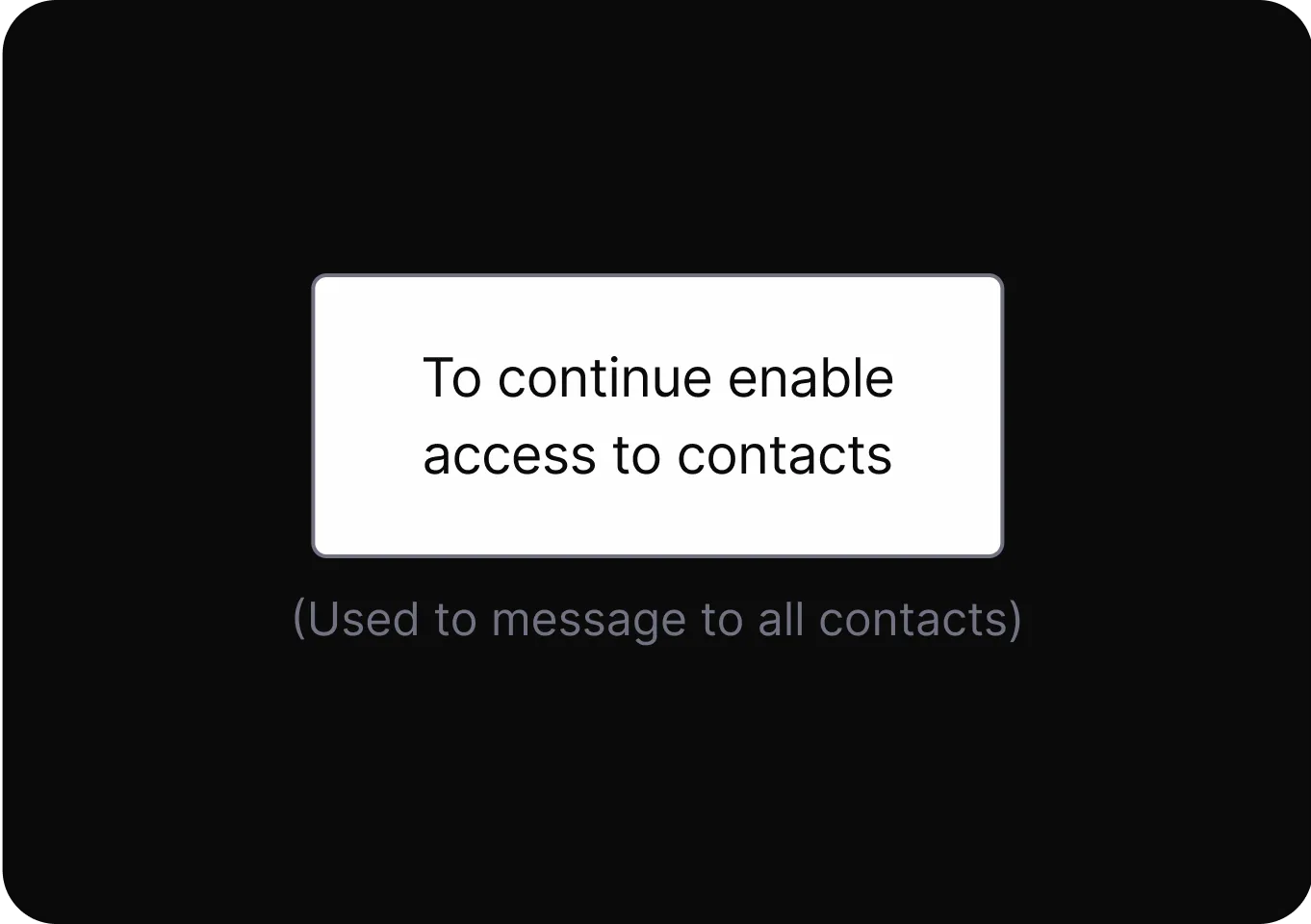
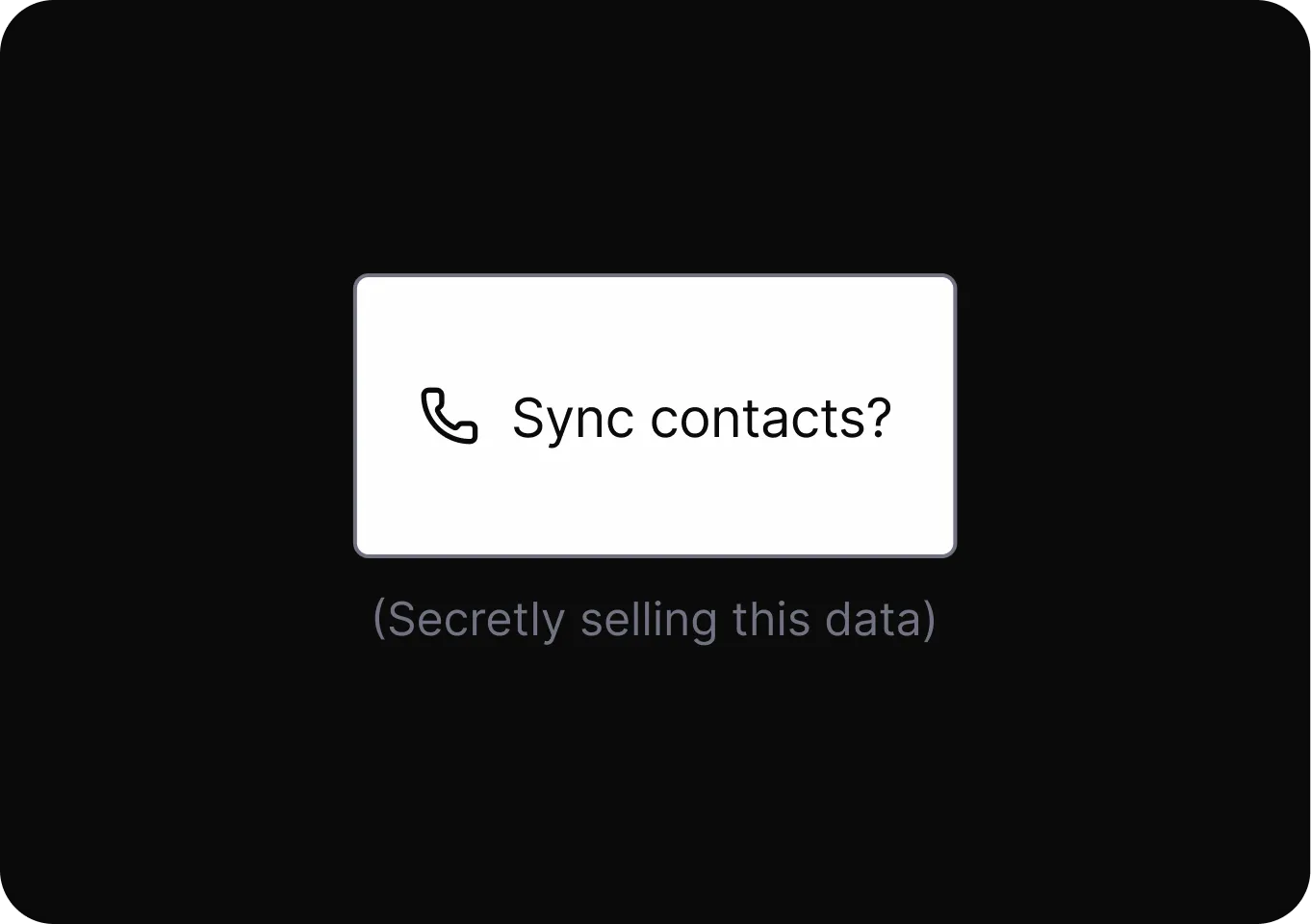
Social Engineering
Exploit cognitive biases to increase the likelihood of a desired action.
-
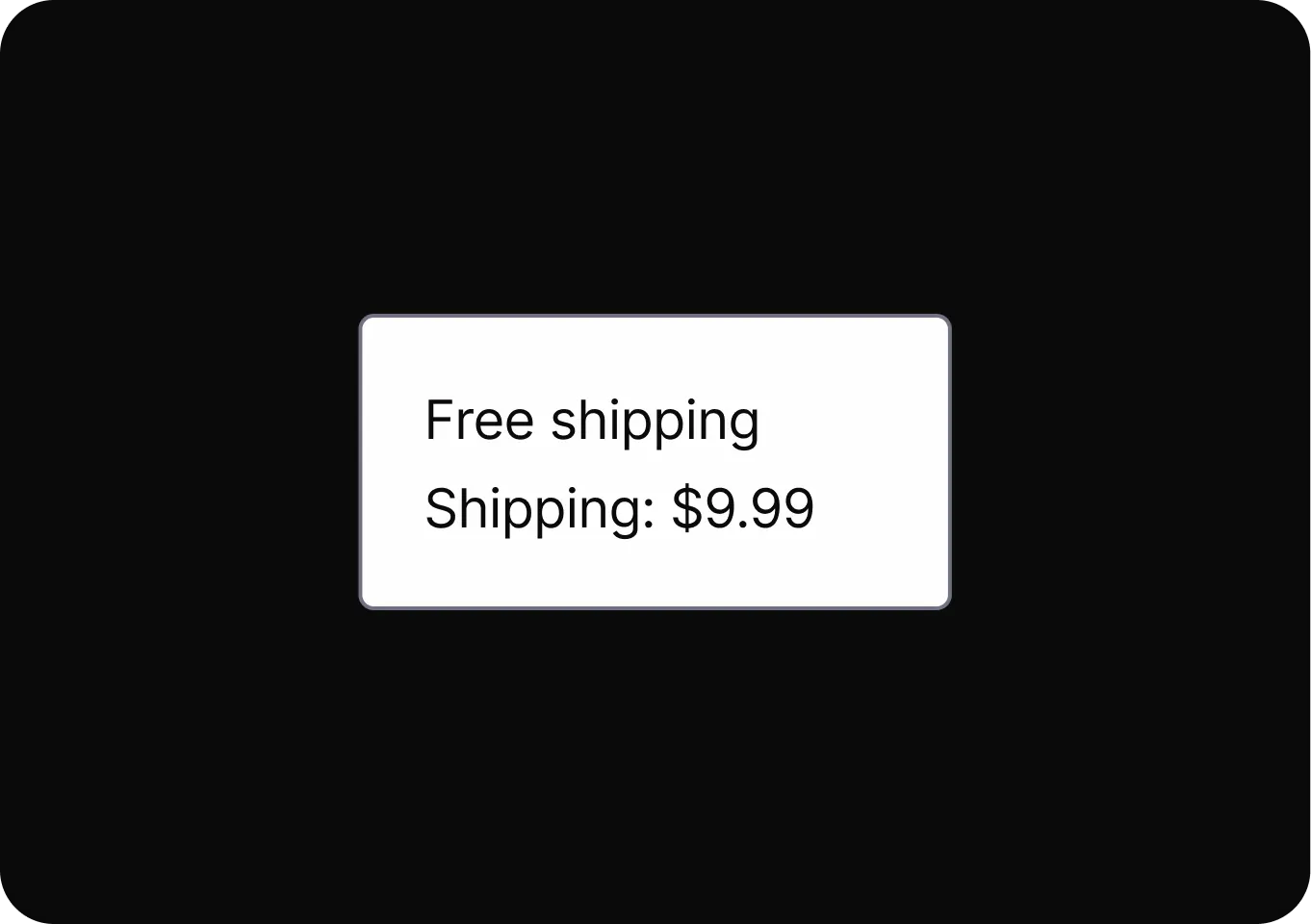
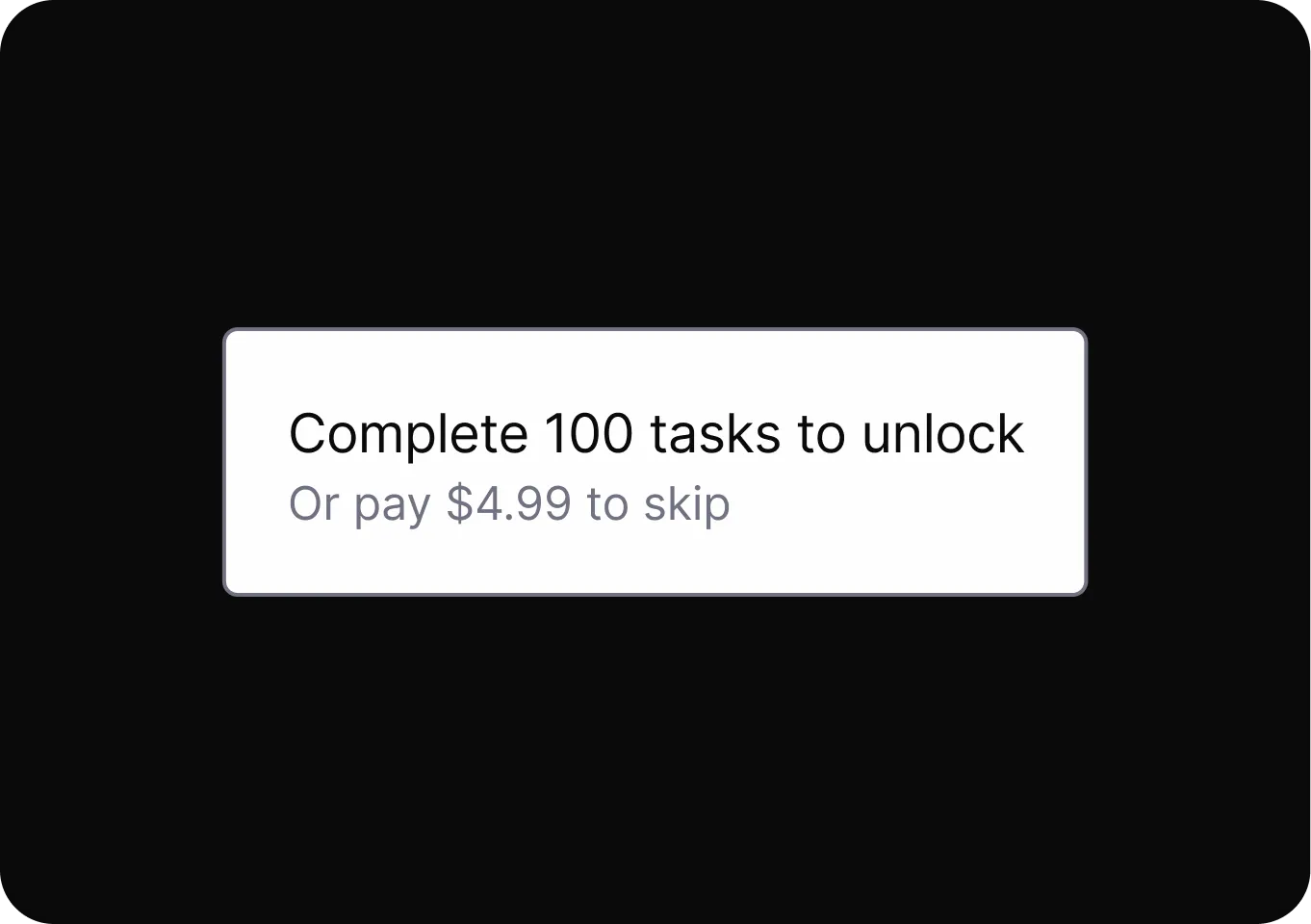
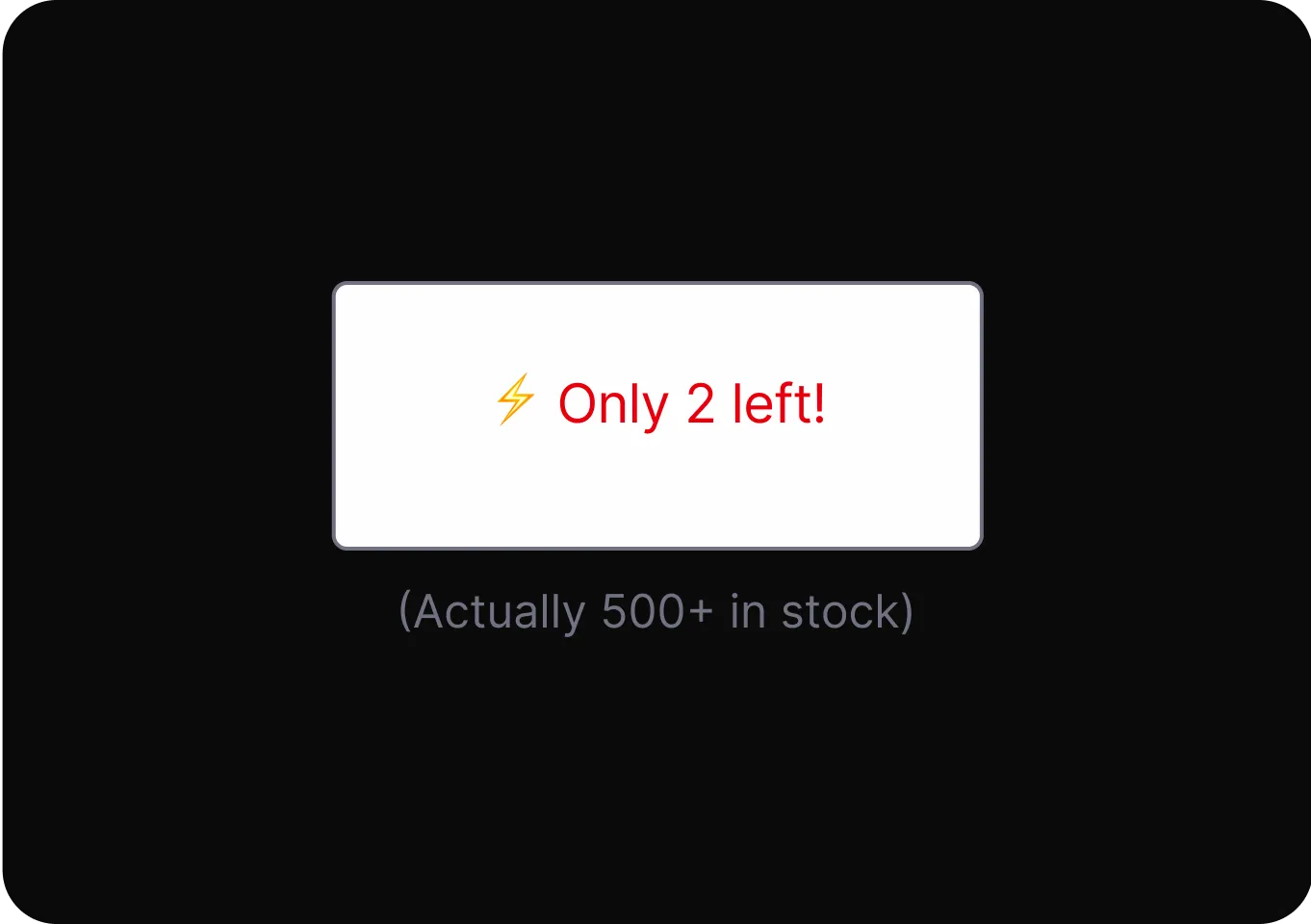
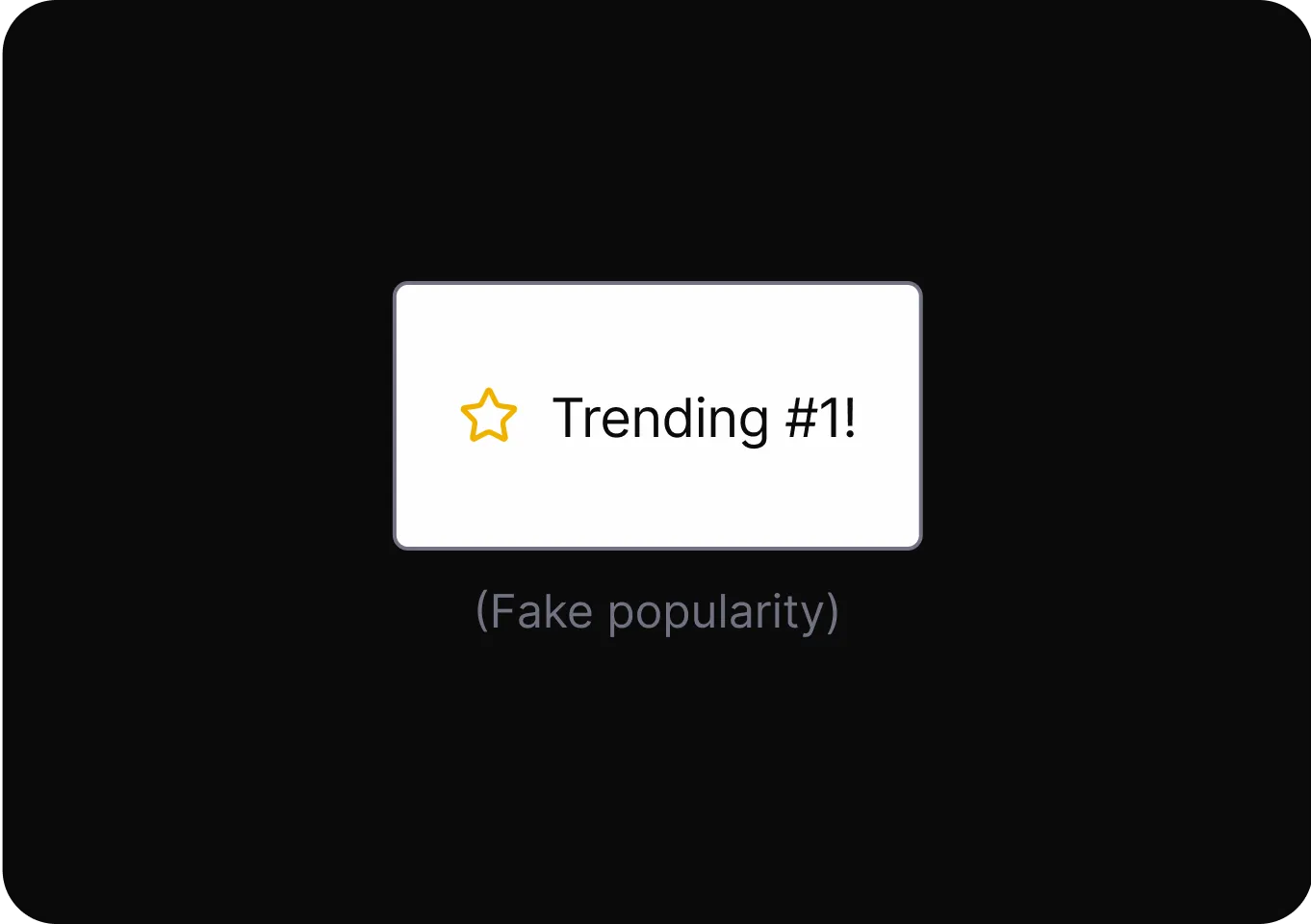
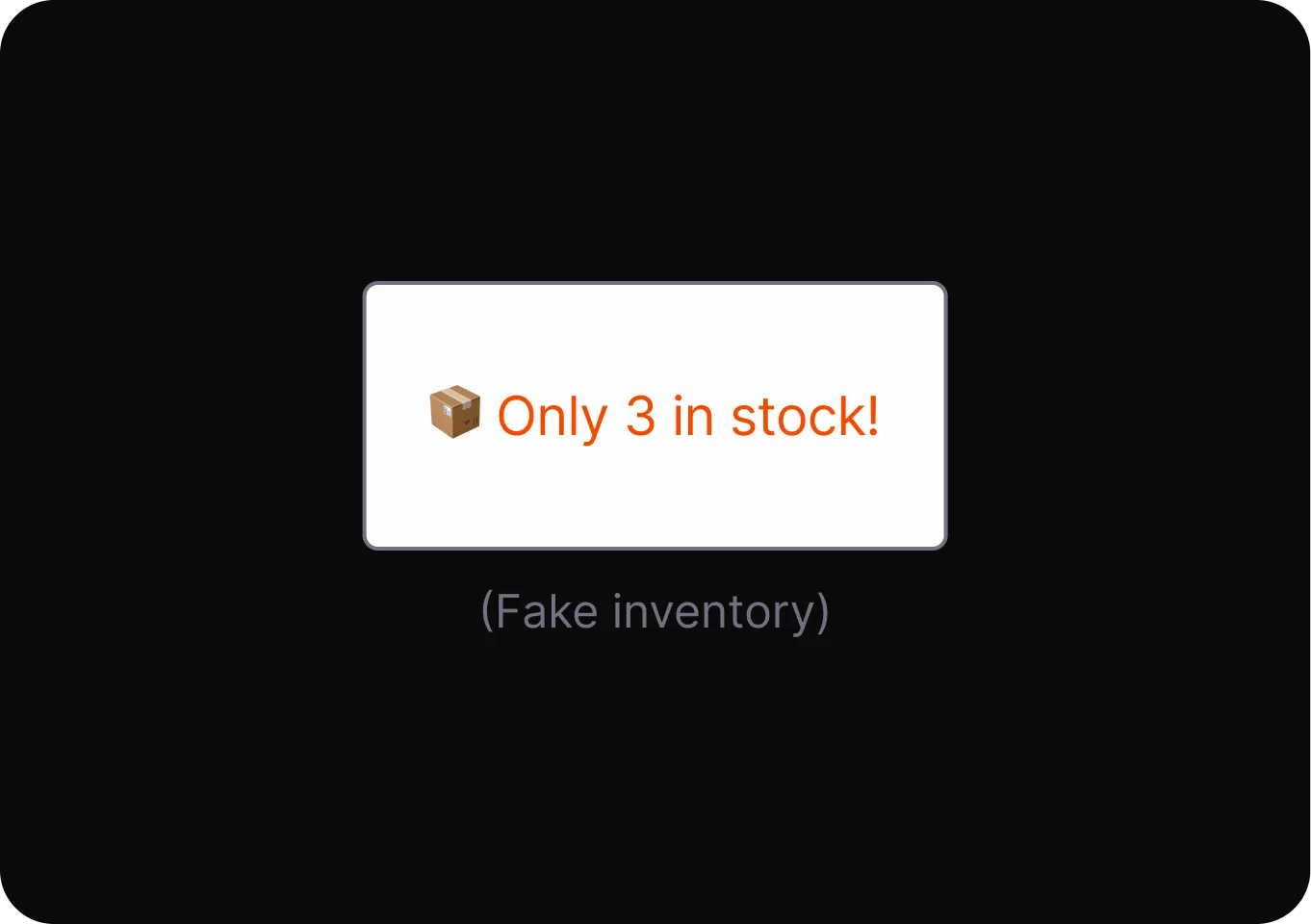
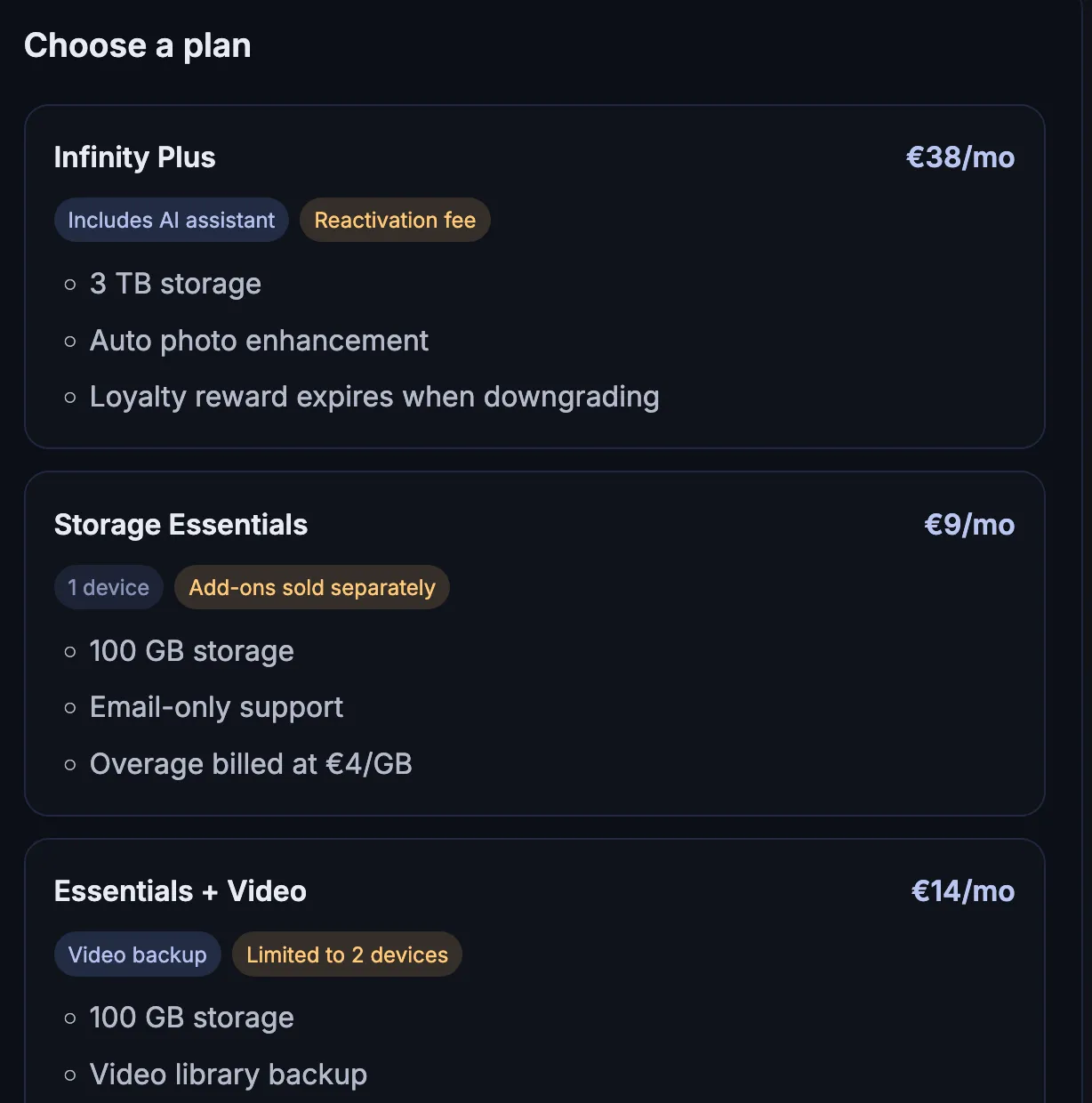
Scarcity and Popularity Claims
It pressures users to buy quickly by presenting products as highly sought-after or in limited supply, increasing urgency and perceived value.
- High Demand It presents a product as highly sought-after or nearly sold out to pressure users into buying based on false urgency.
-
-
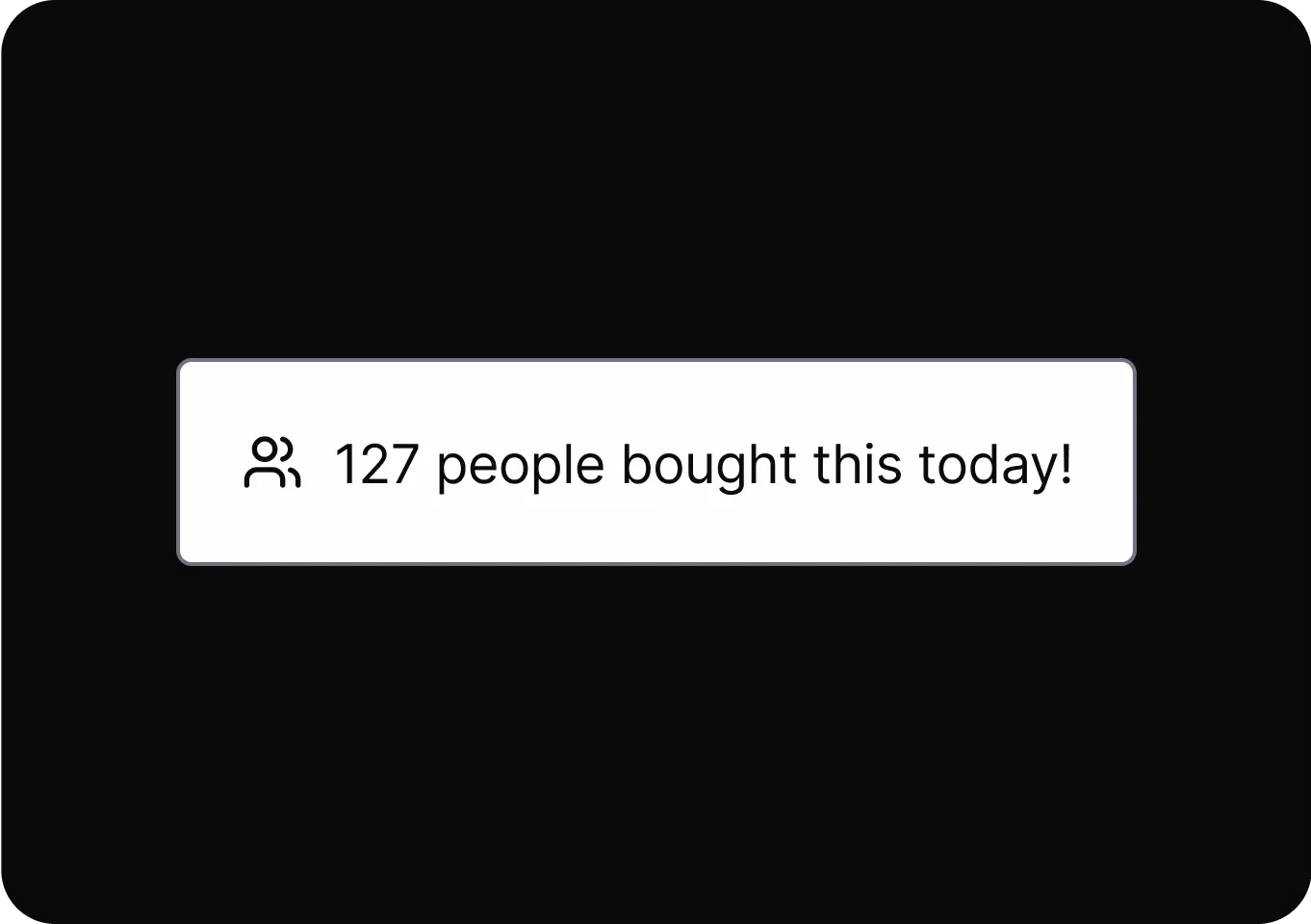
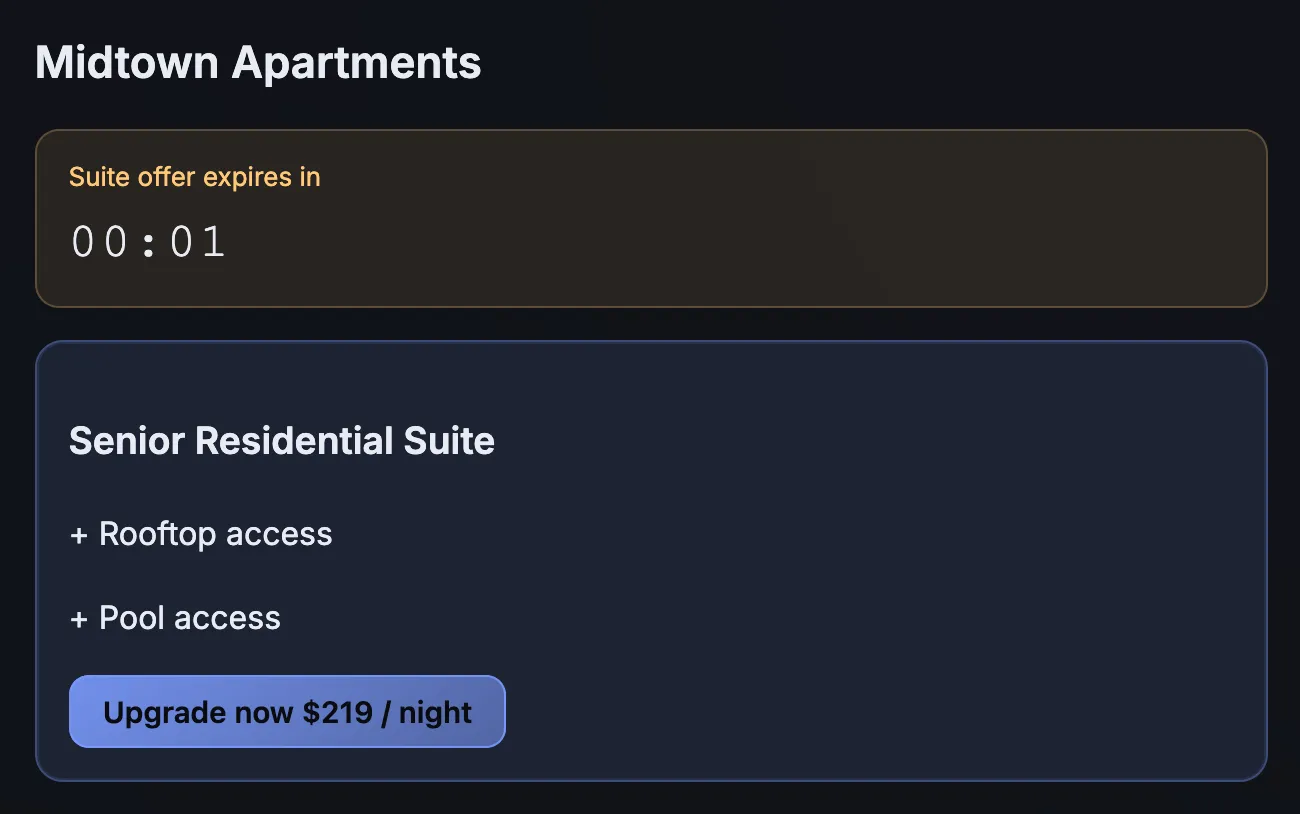
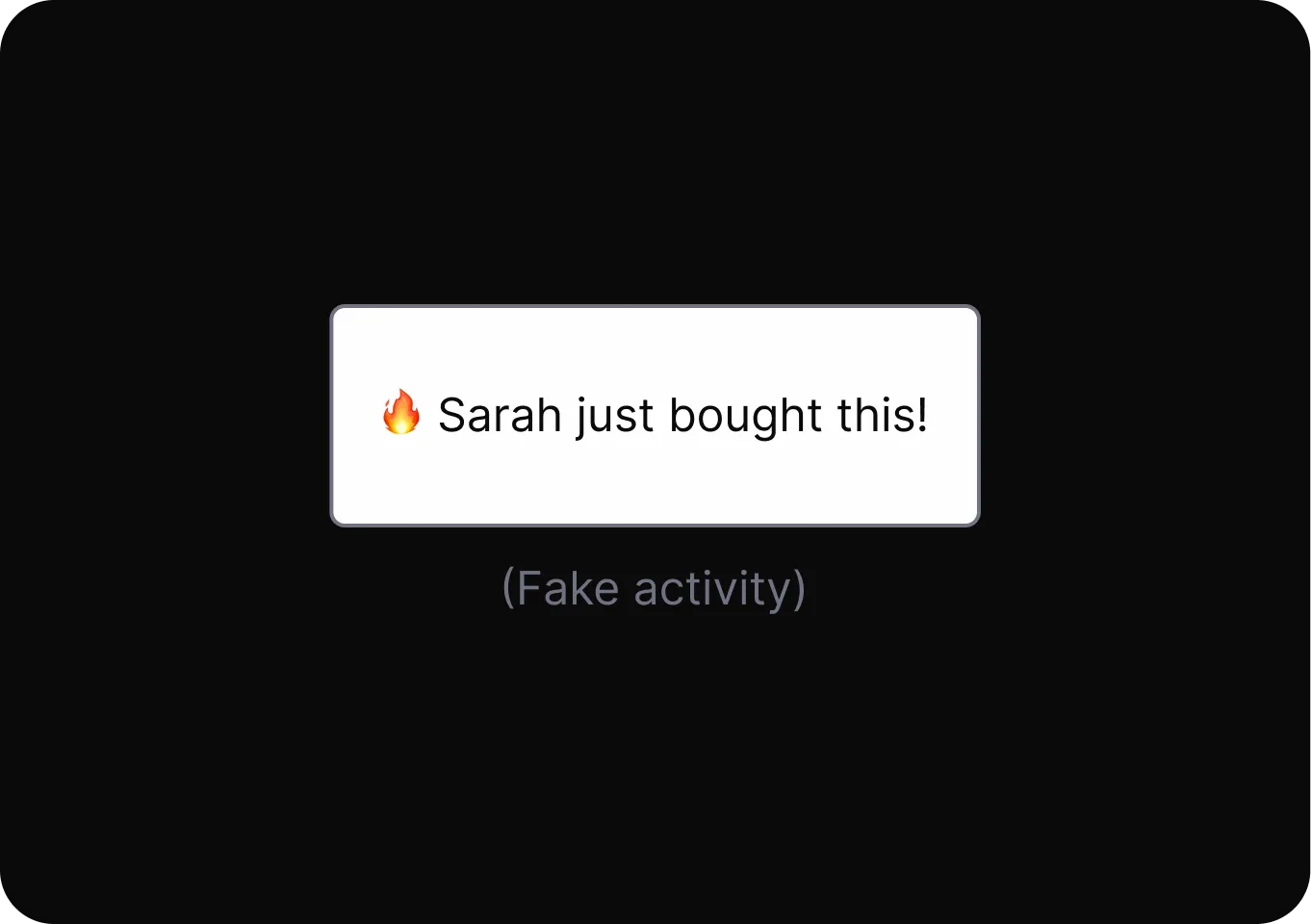
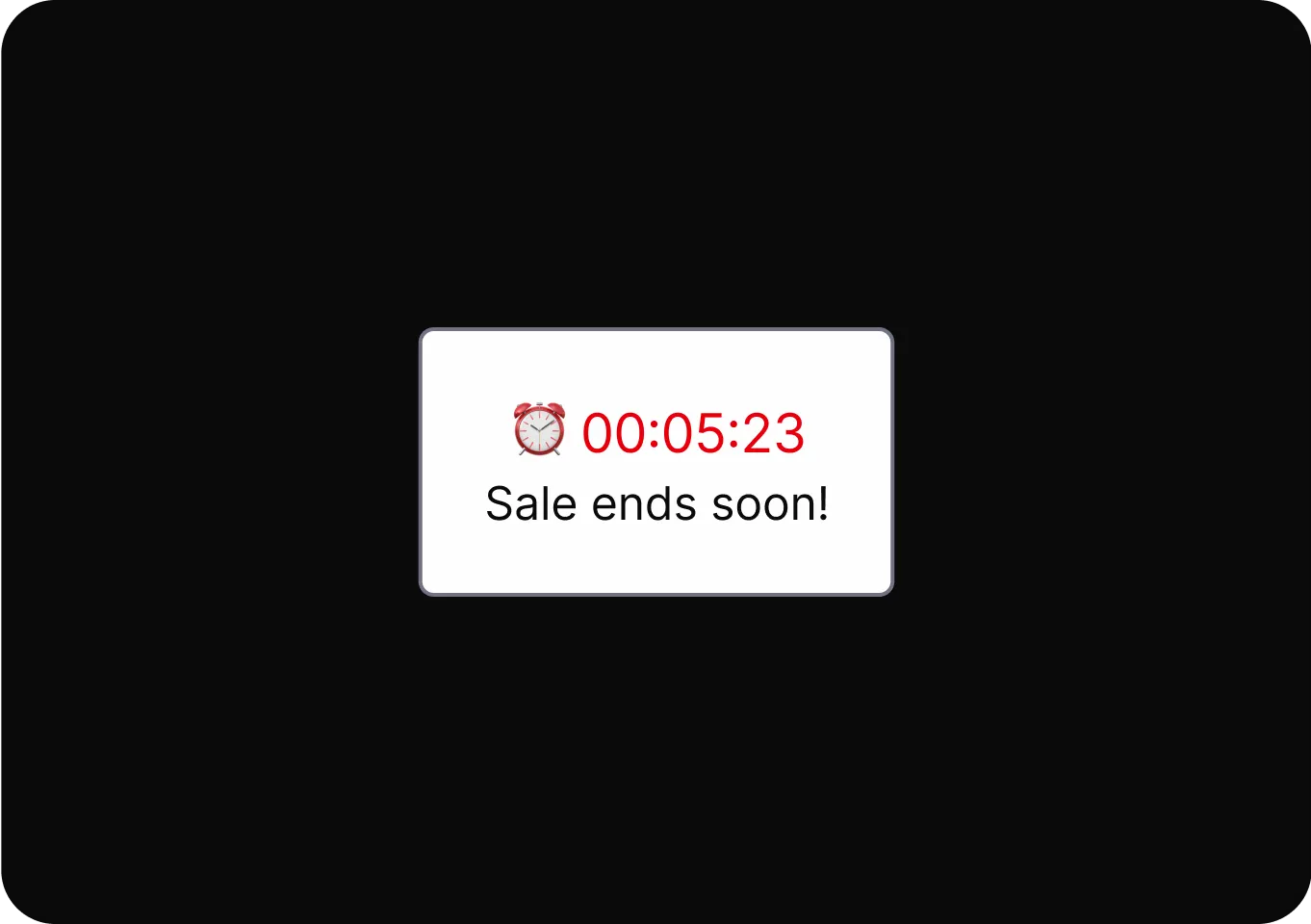
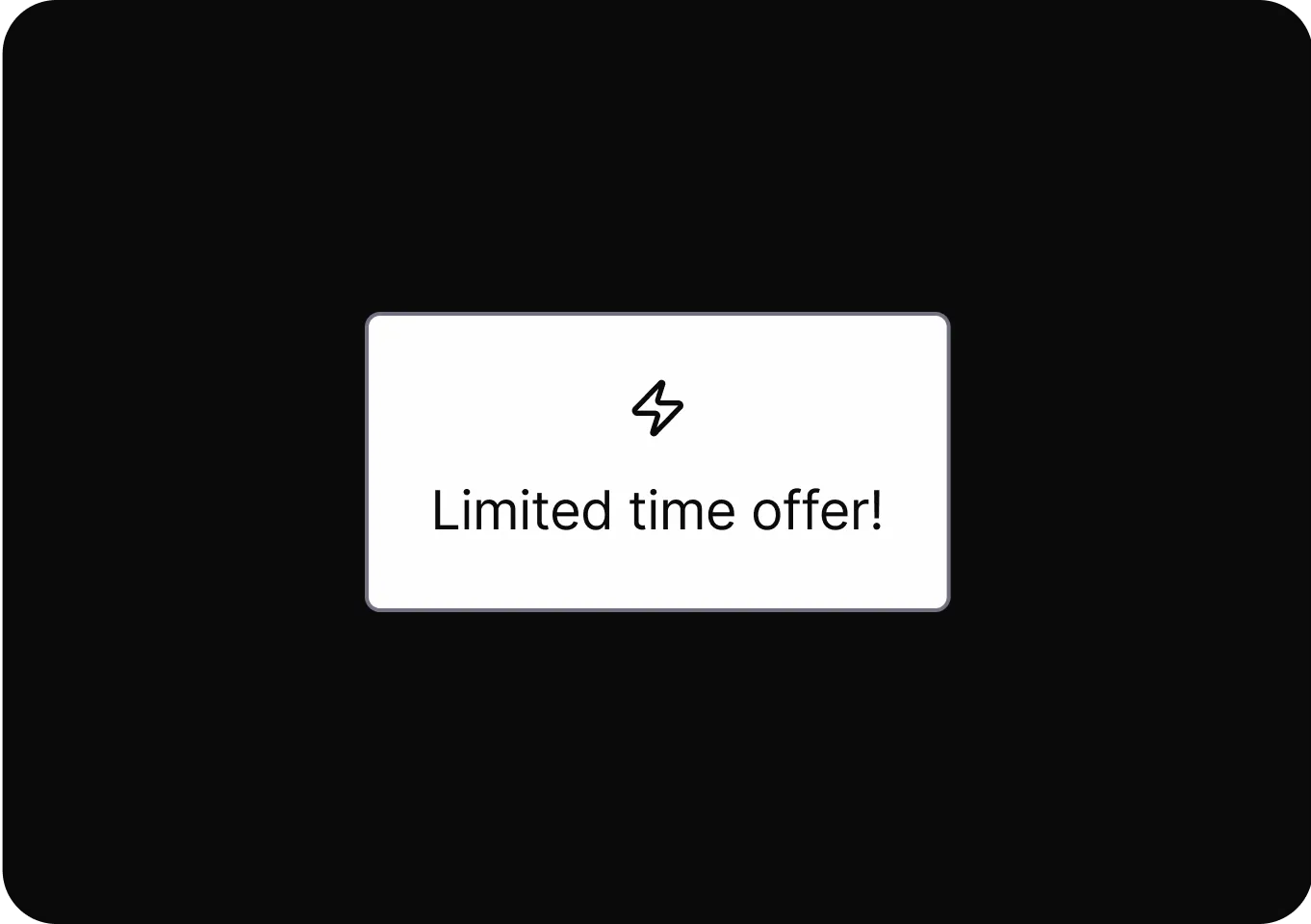
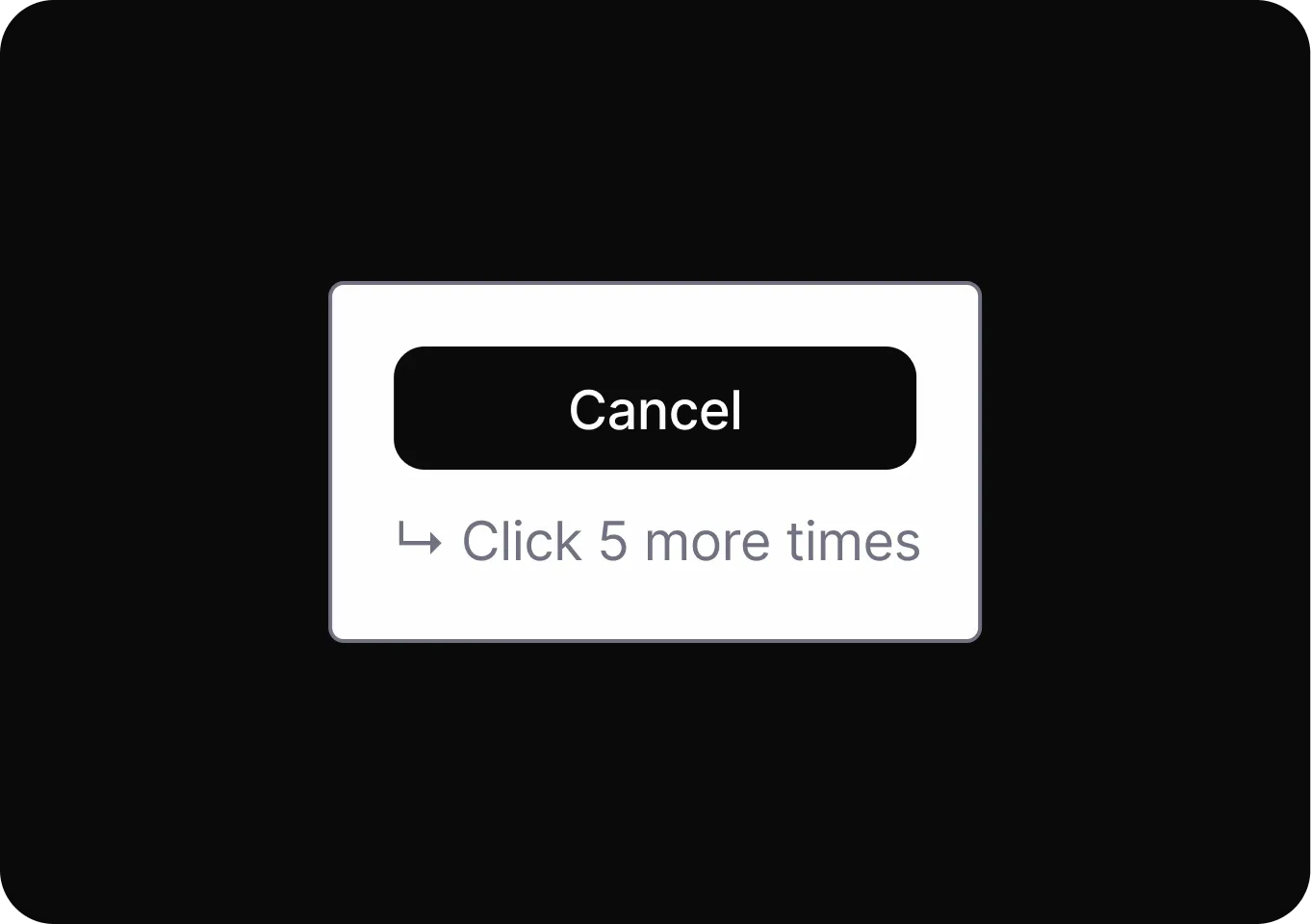
Urgency
It accelerates user decisions by prompting immediate action through time-sensitive or limited availability cues.
- Activity Messages Displays misleading notifications about others’ actions to create urgency and pressure users into making quick decisions.
- Countdown Timer Displays a fake timer to create urgency and pressure users into making quick, uninformed purchase decisions.
- Limited Time Message Creates urgency by implying an offer will end soon, pressuring users to make quick, uninformed purchases.
-
-
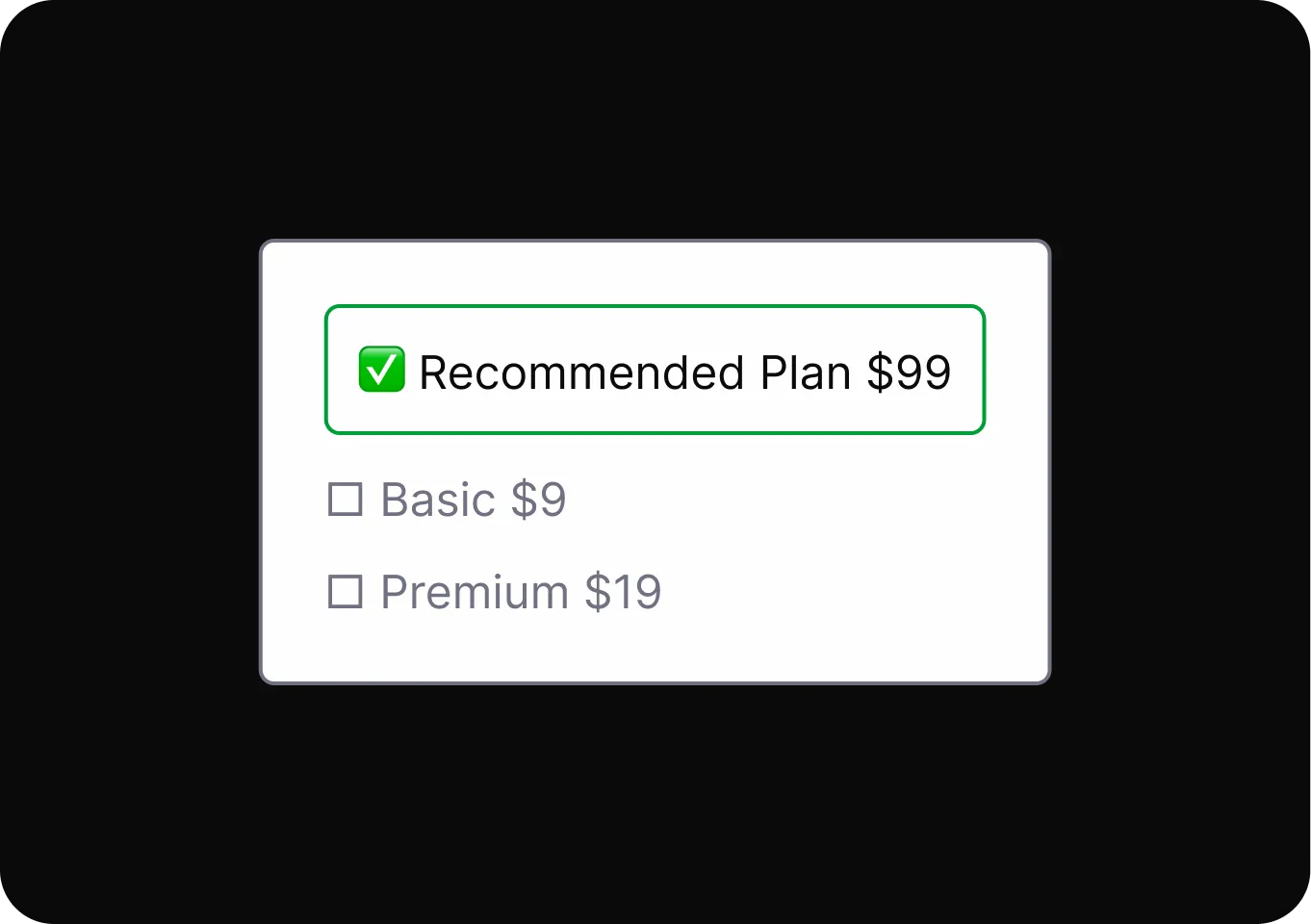
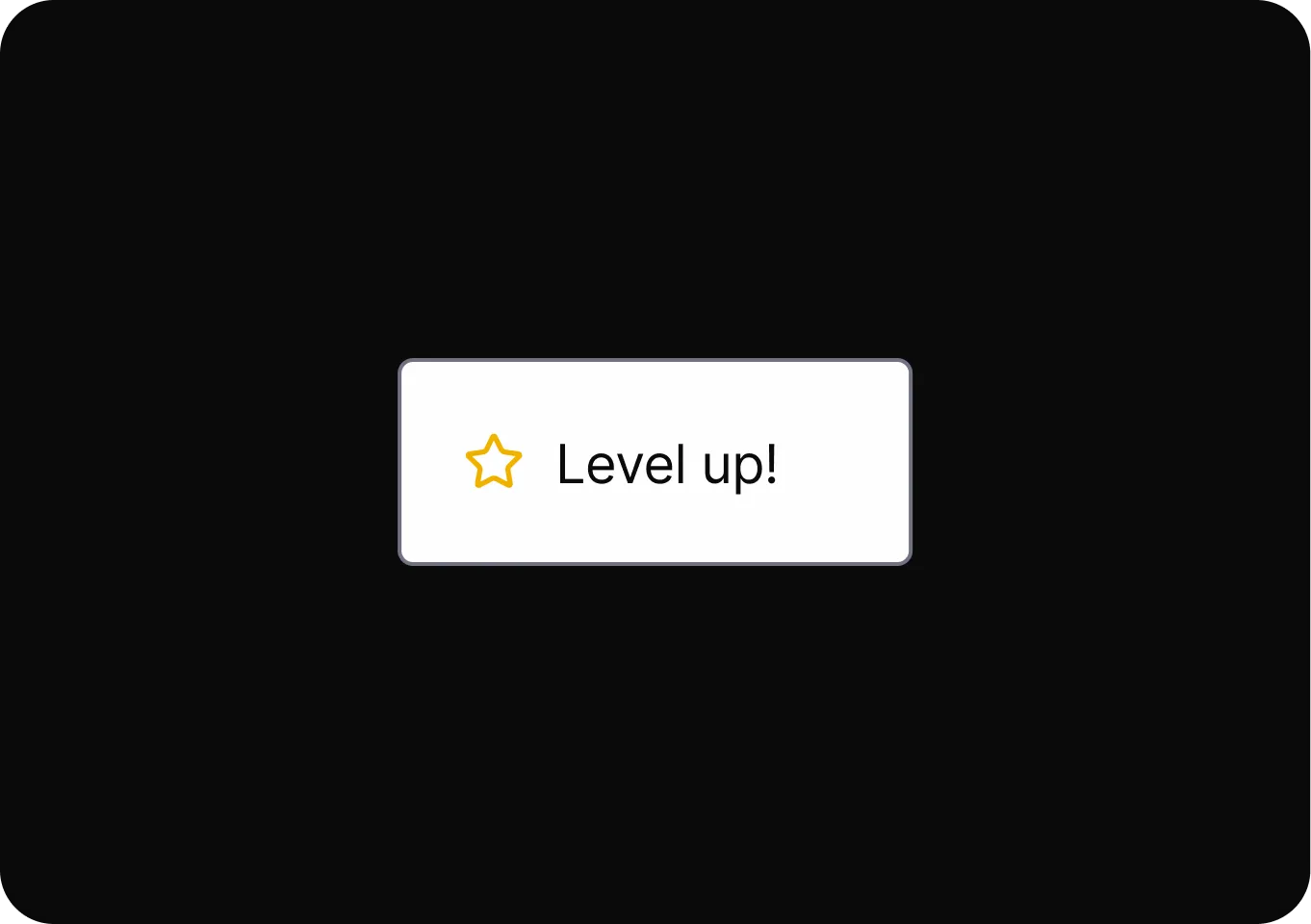
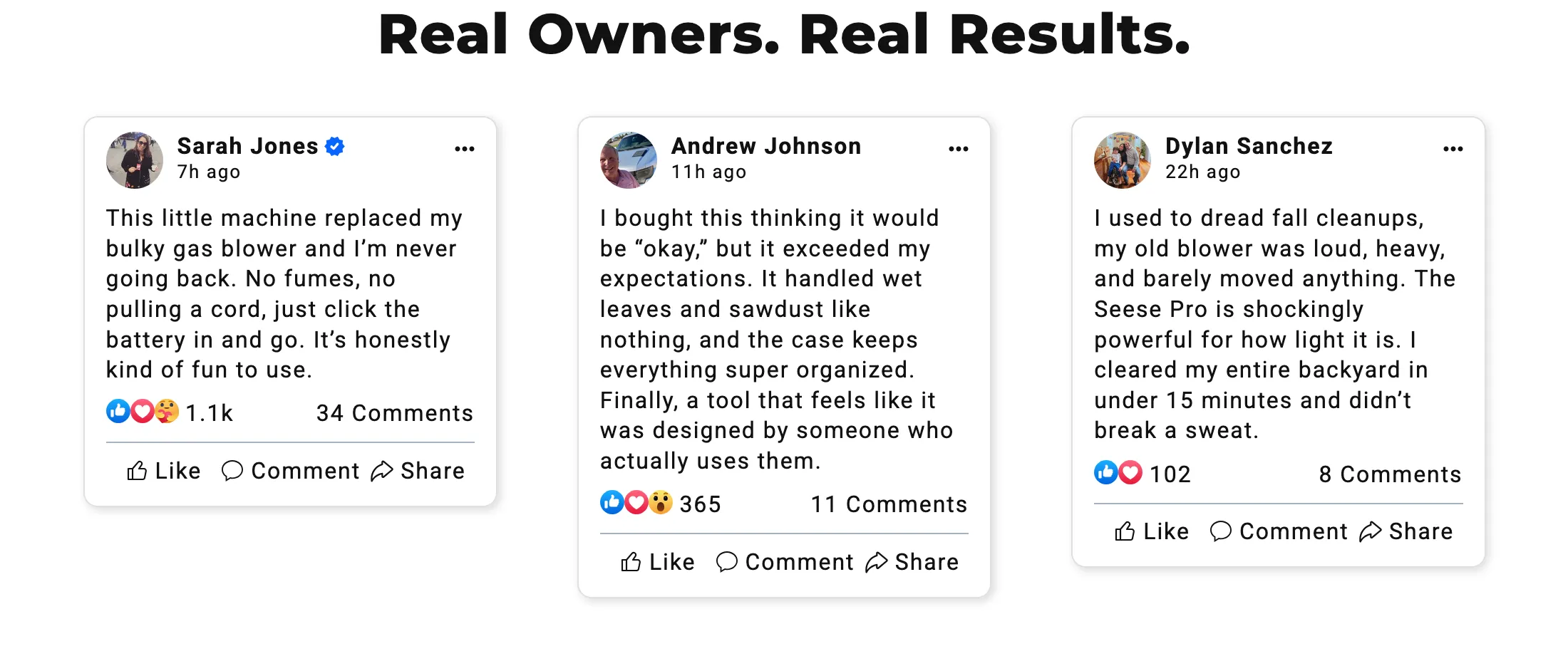
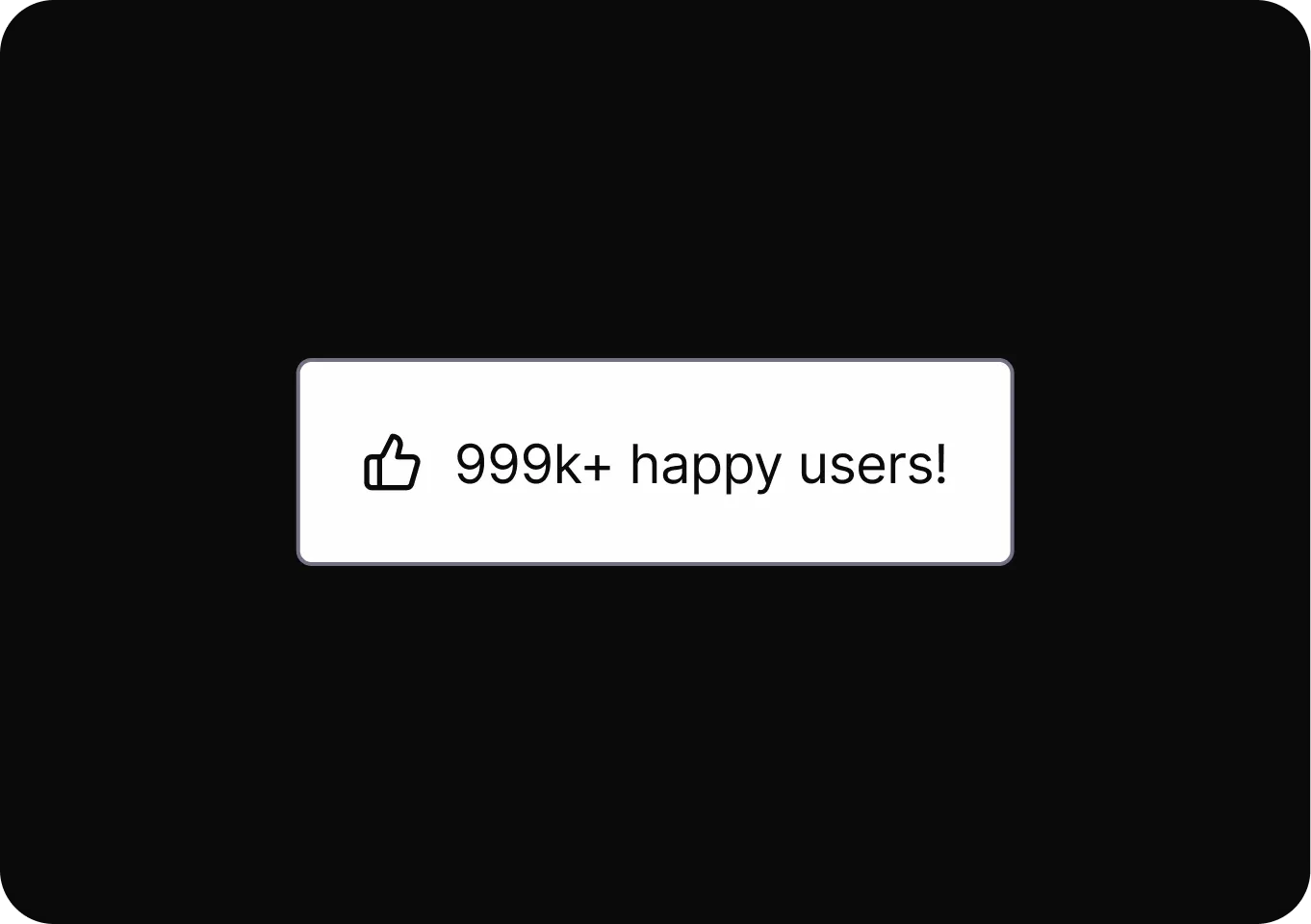
Social Proof
Influences people to quickly follow others’ behaviors or choices, often leading to decisions based on perceived group consensus.
- Low Stock Displays a false claim of limited product quantity to create urgency and pressure users into making quick purchase decisions.
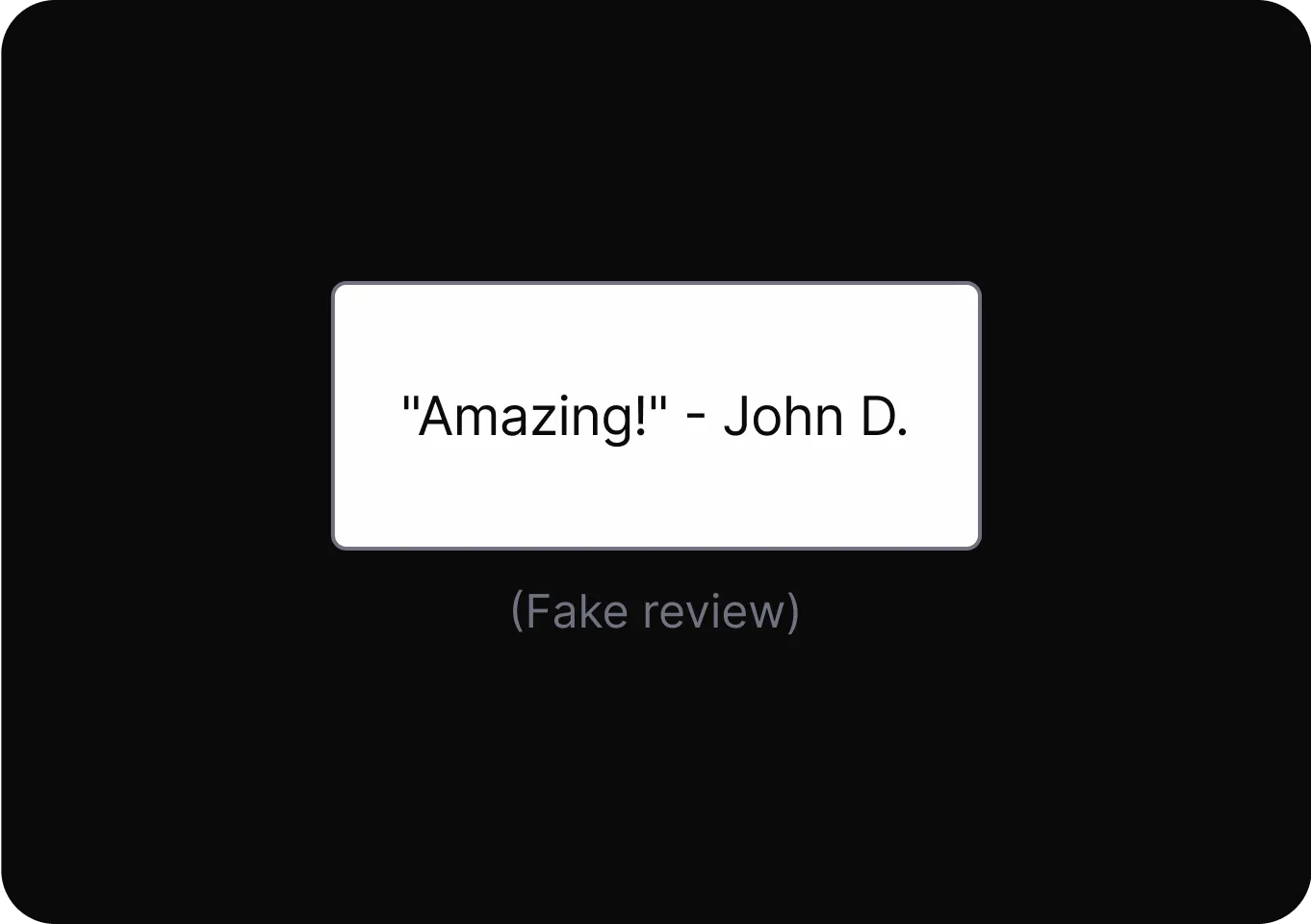
- Endorsements and Testimonials It presents positive opinions from others to influence decisions, even when those opinions may be unreliable or misleading.
- Parasocial Pressure It encourages trust in a product or service by presenting endorsements from familiar figures, regardless of endorsement accuracy.
-
-
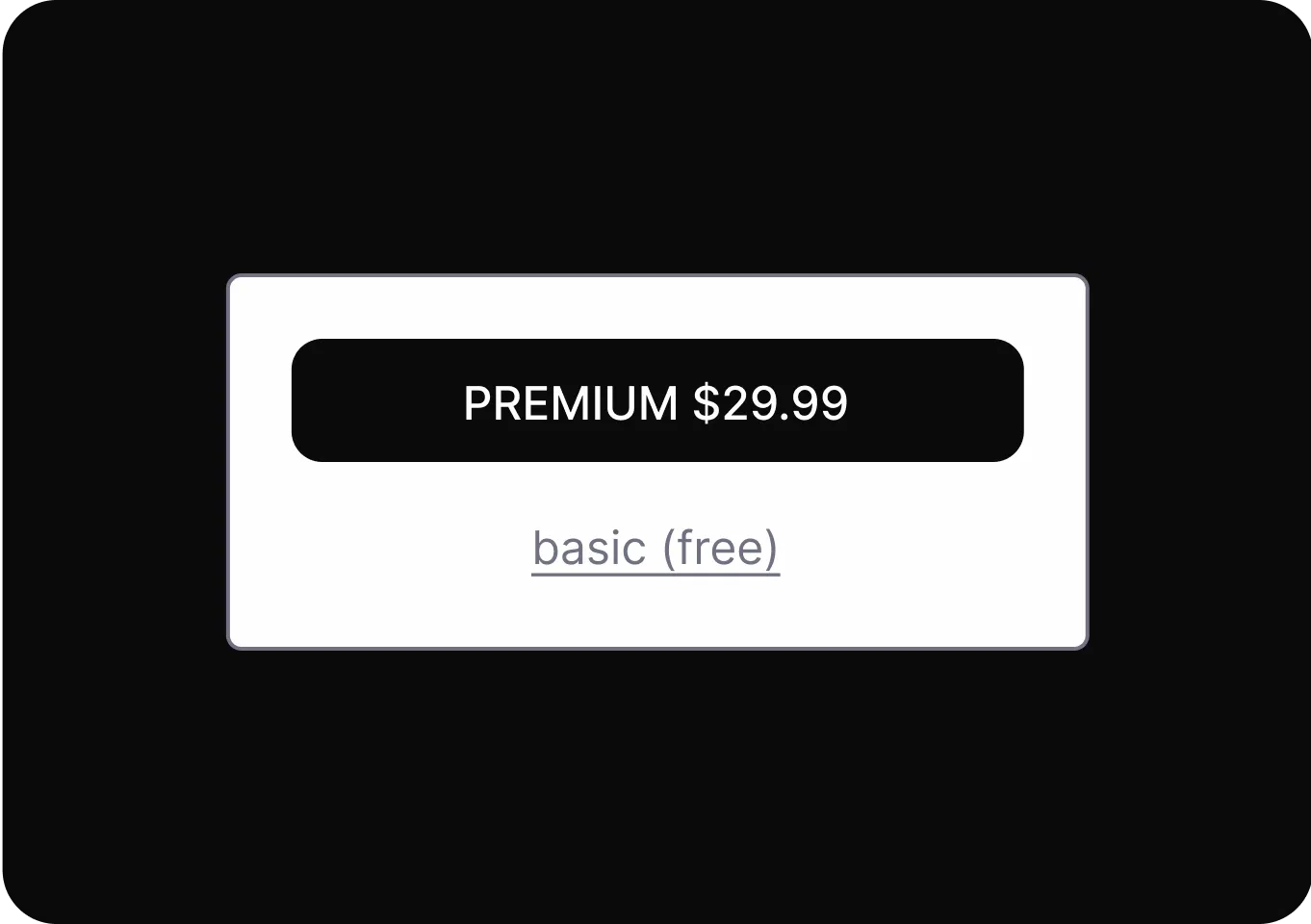
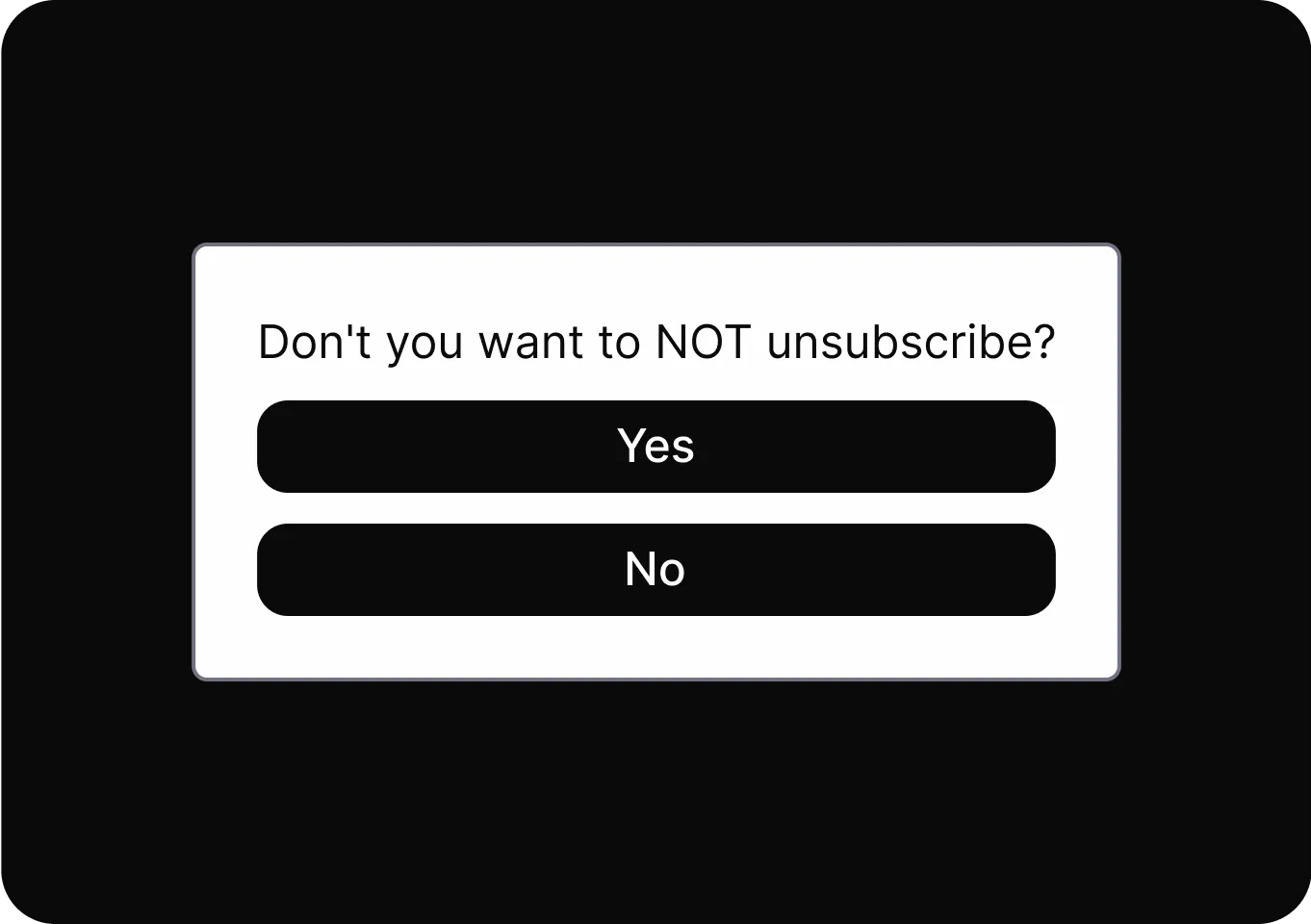
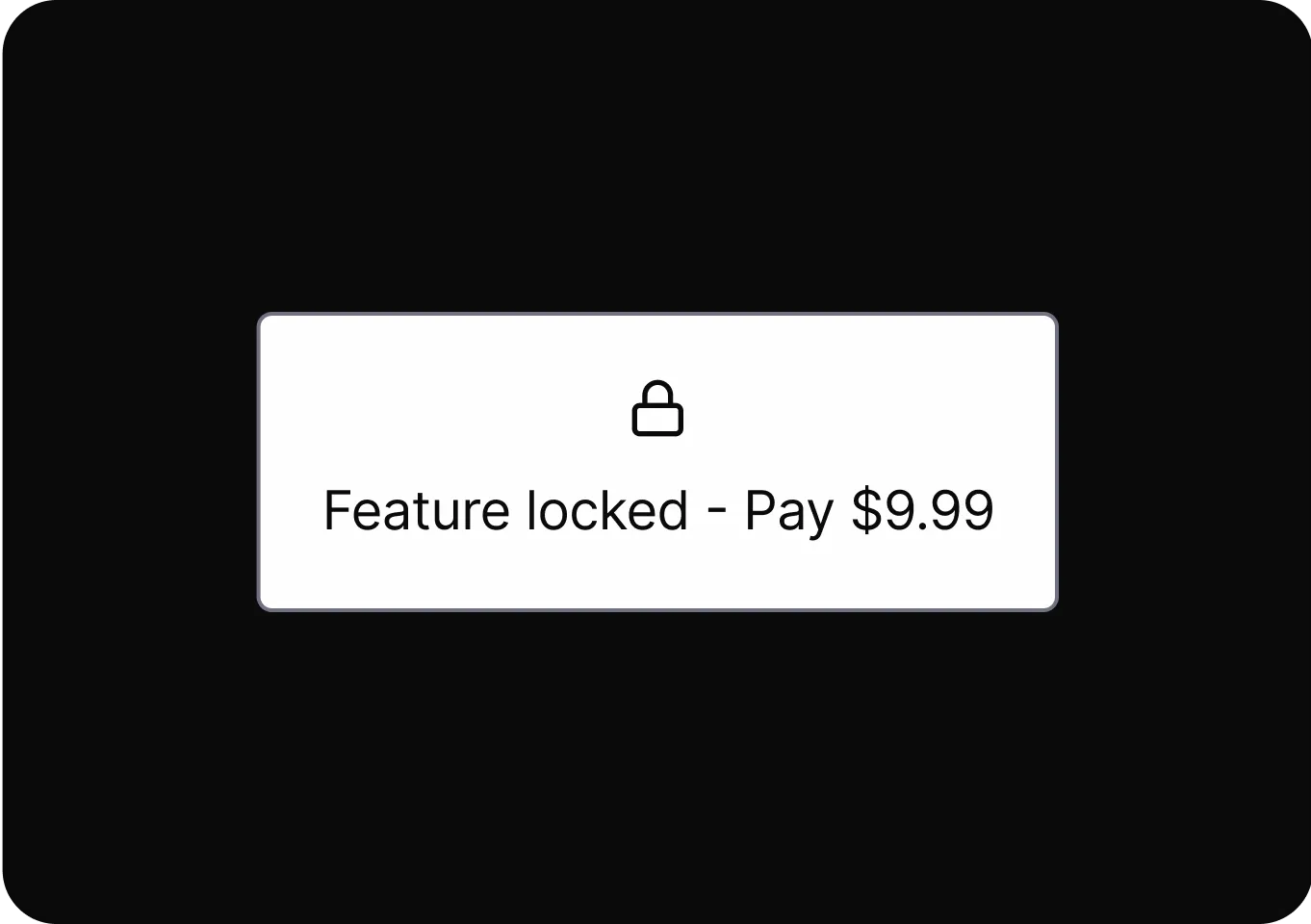
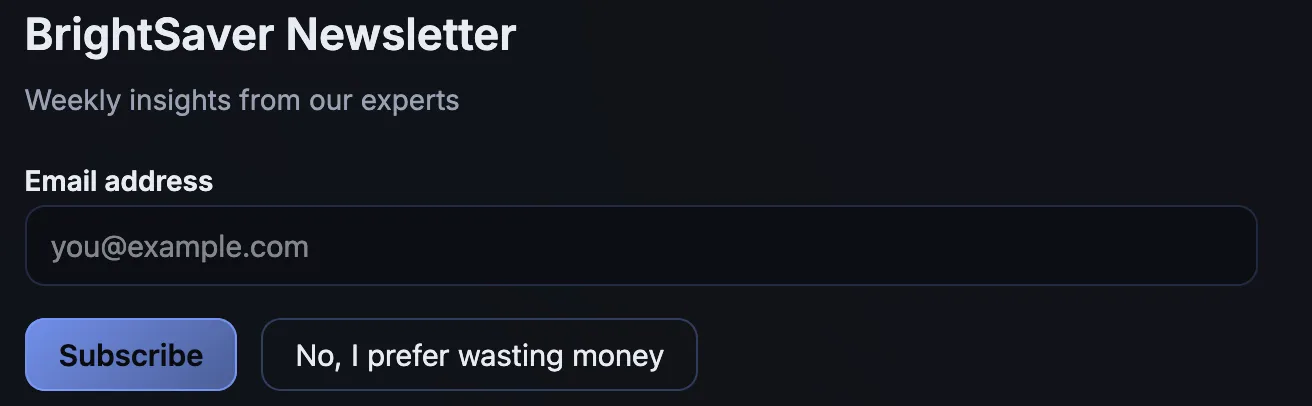
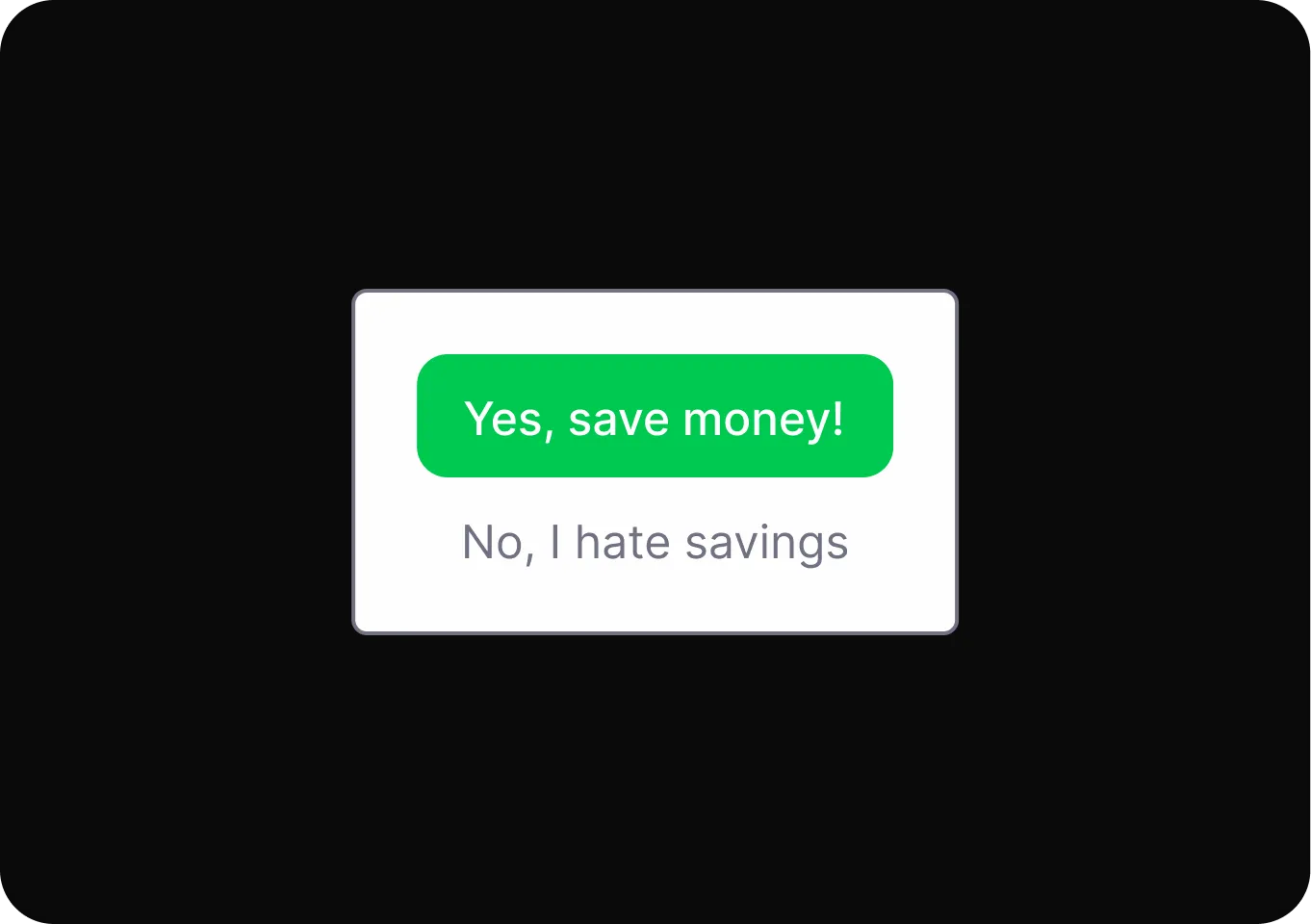
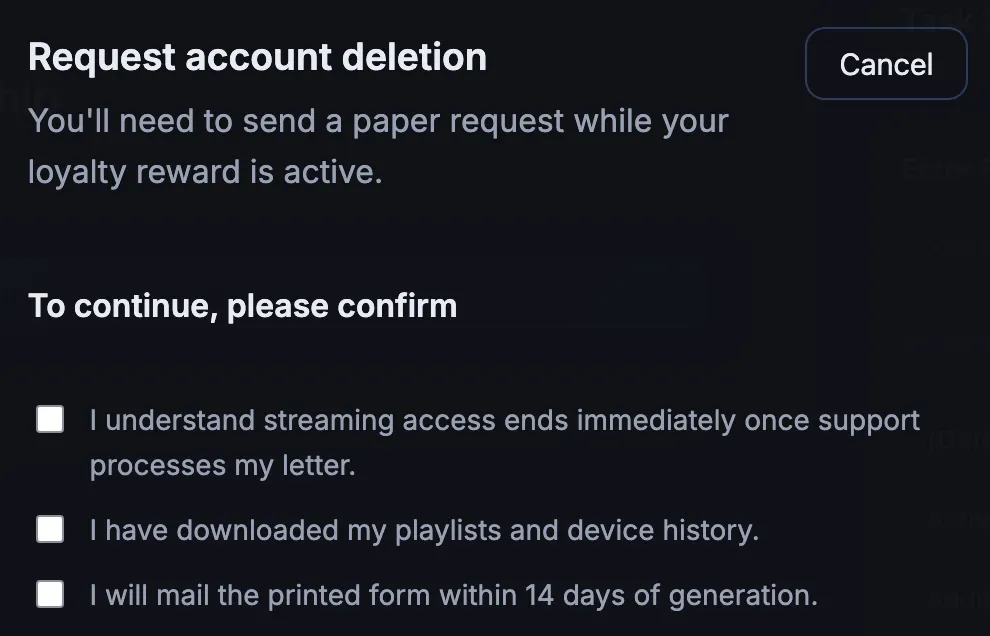
Shaming
Uses emotional pressure to make users feel guilty or inadequate if they do not choose a specific option.
- Confirmshaming Uses guilt-inducing language to pressure users into making a specific choice by manipulating their emotions.
-
-
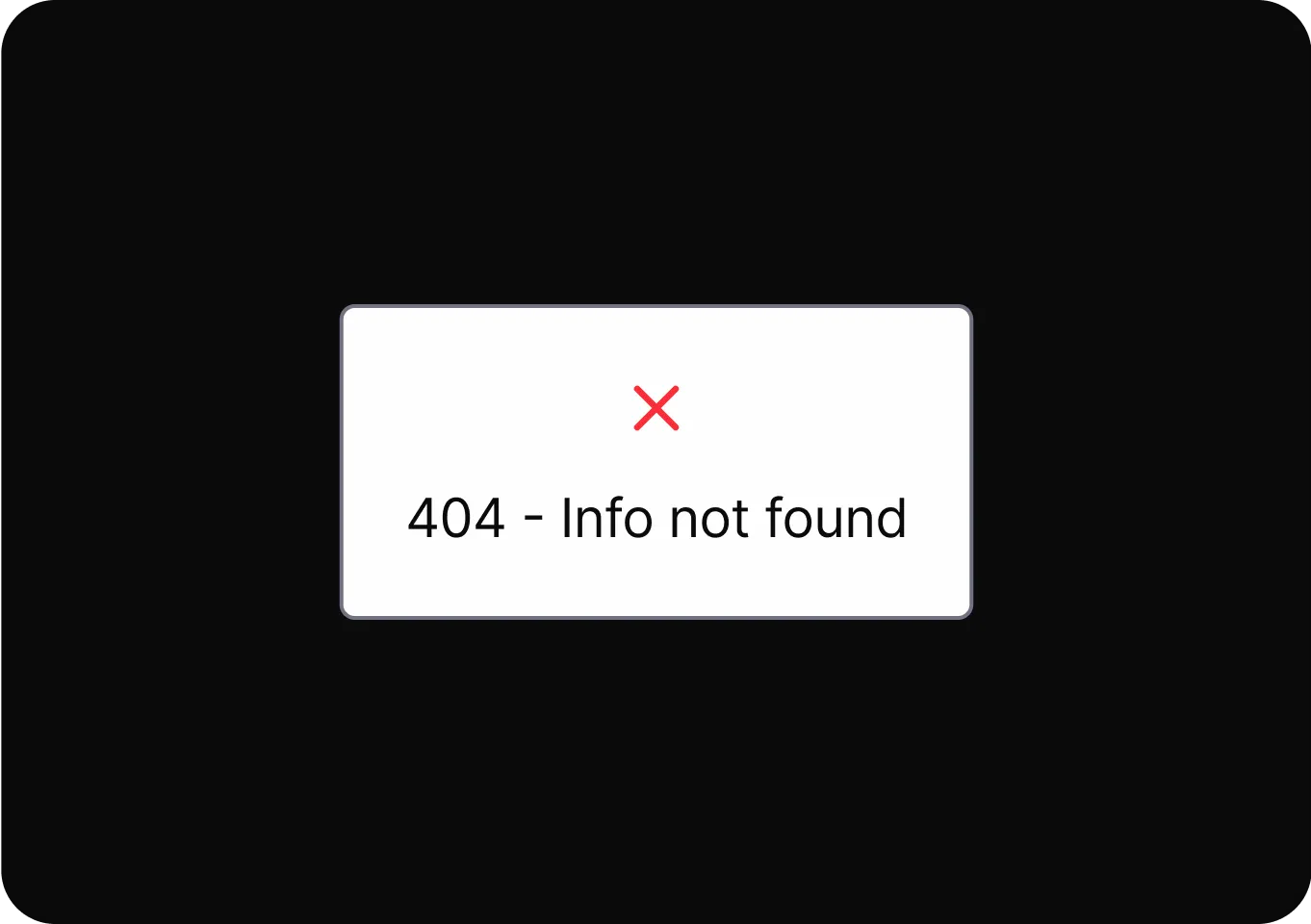
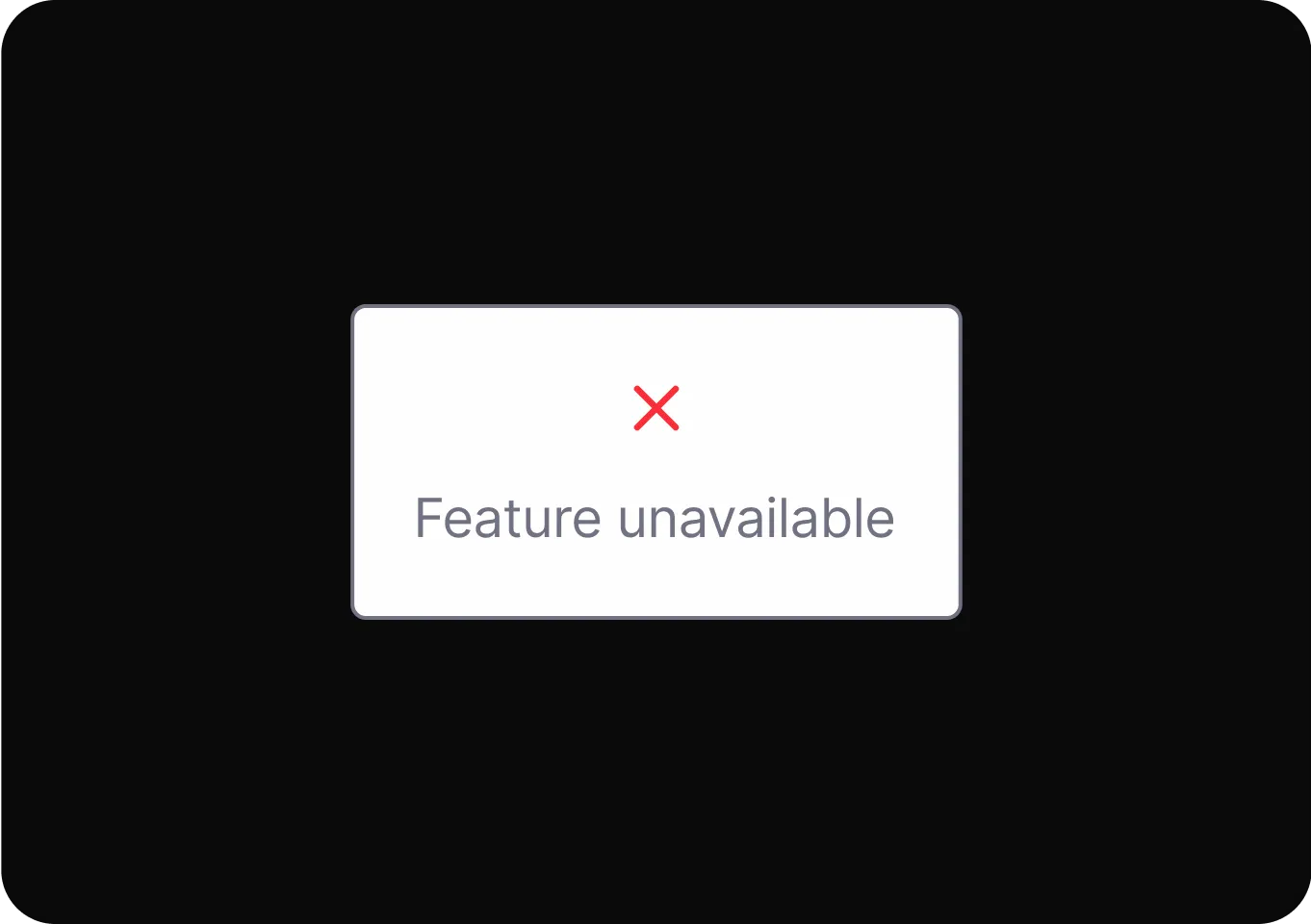
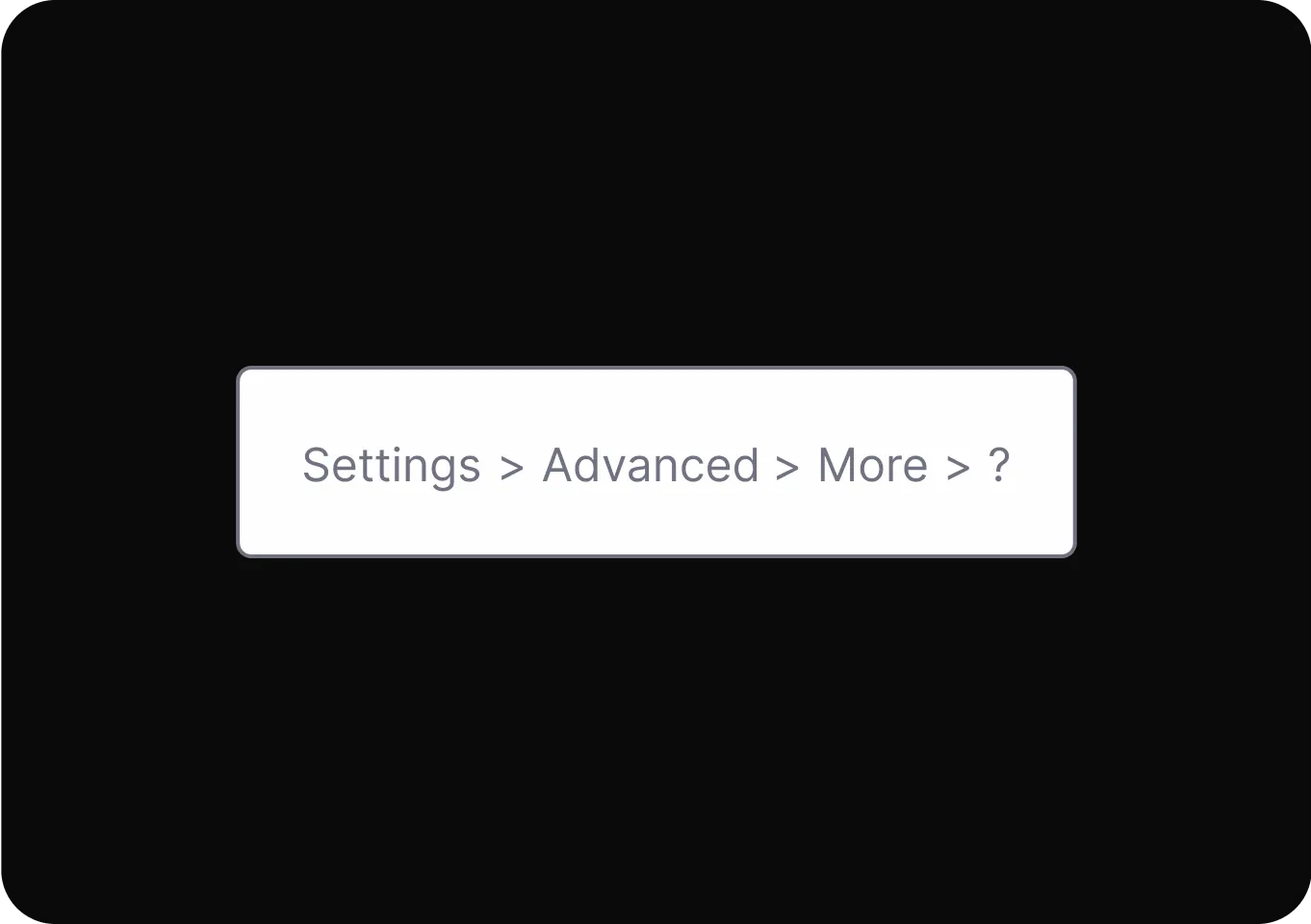
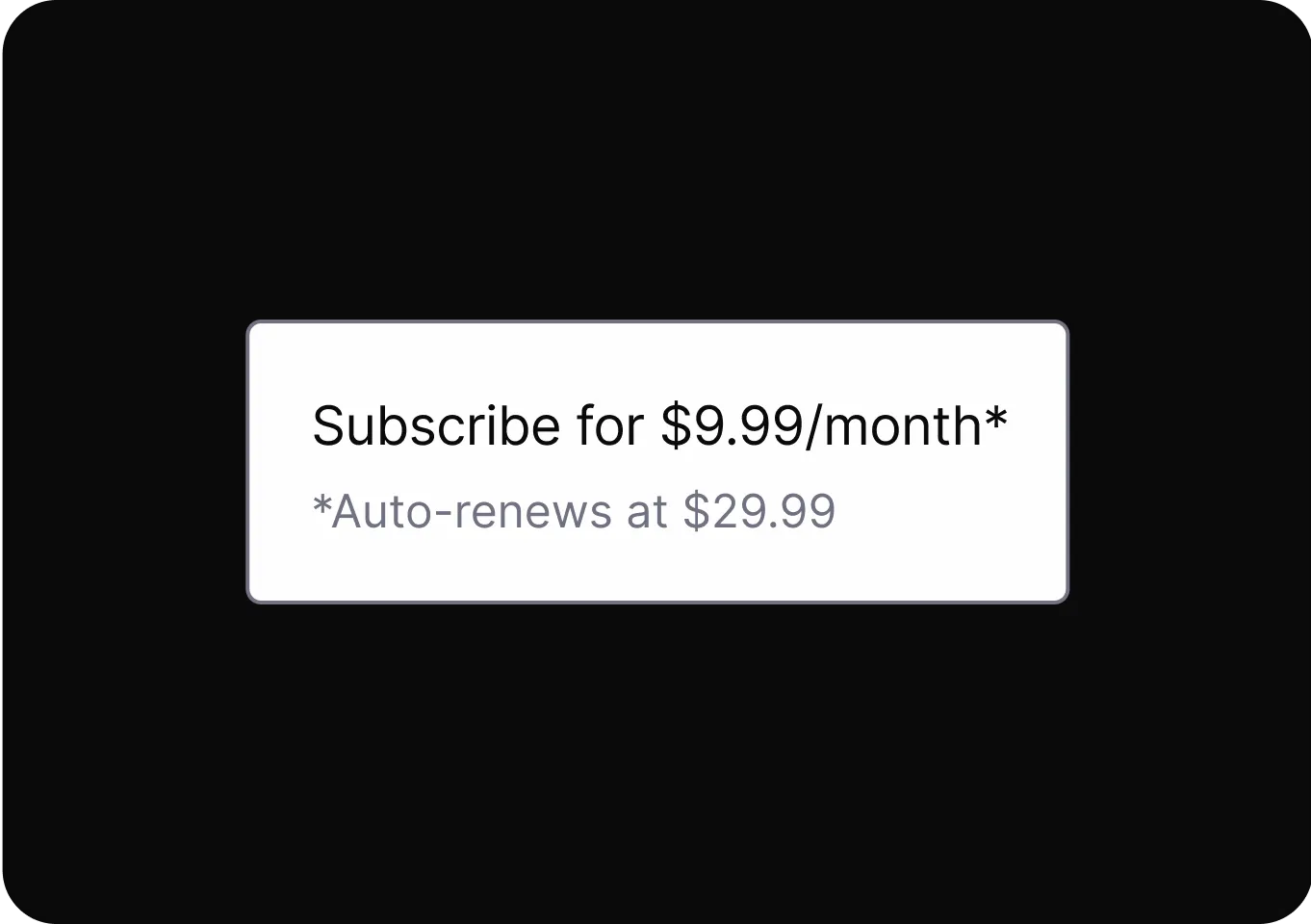
Personalization
It uses personal data to shape user experiences, influencing choices and hiding alternatives to guide user behavior.

















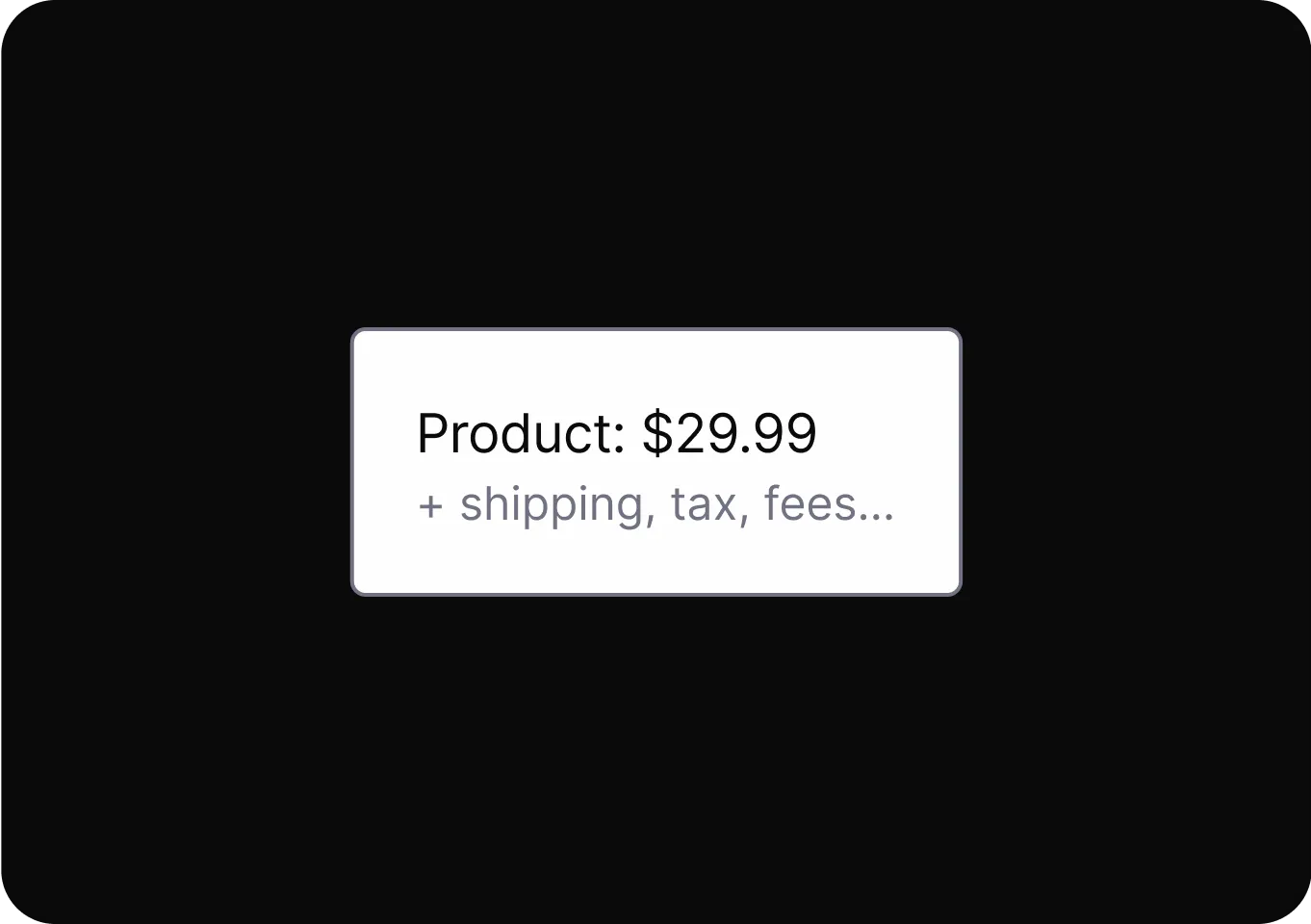

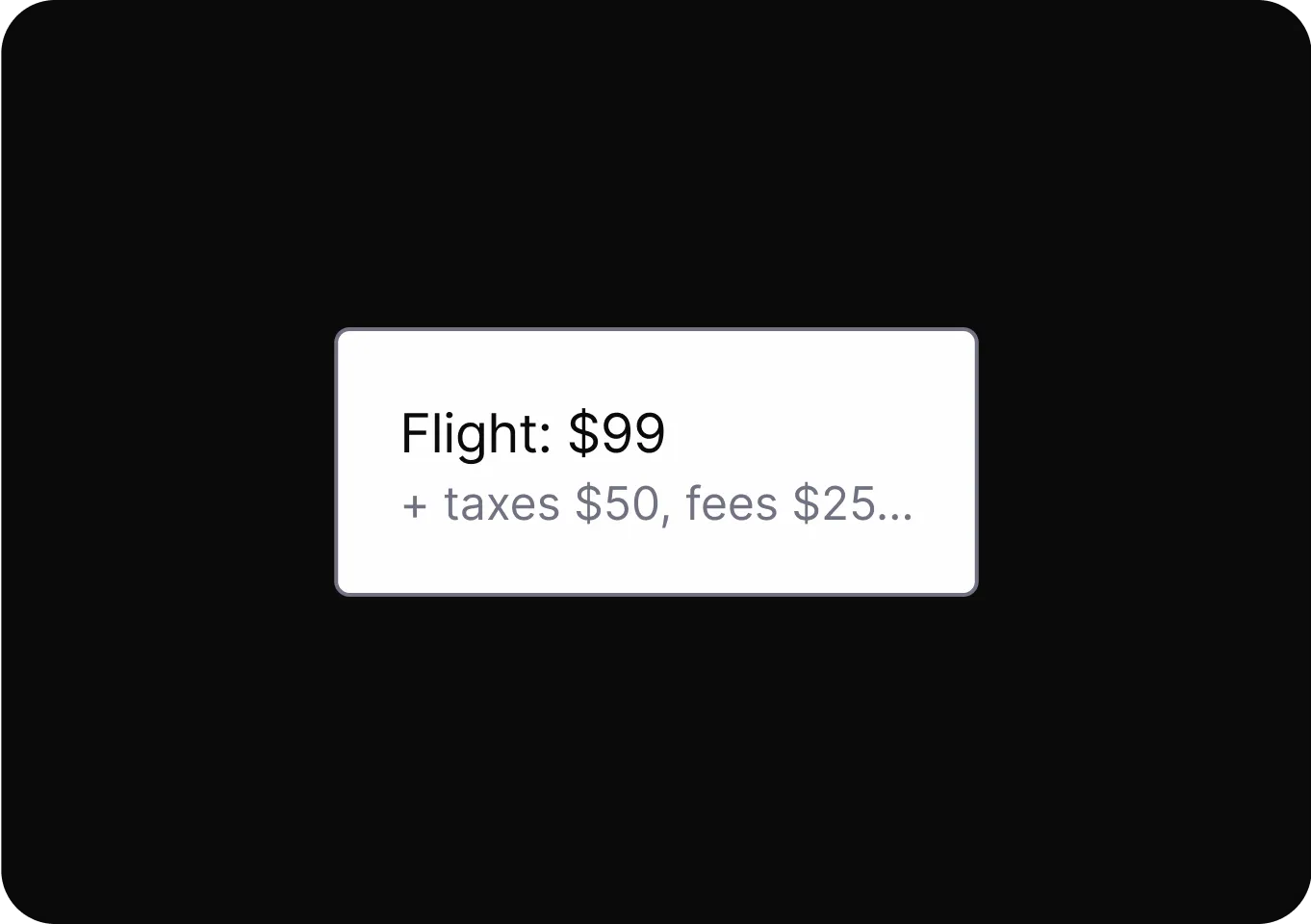
contextualizing%20Cues.DrftjXAS_Z1tn863.webp)